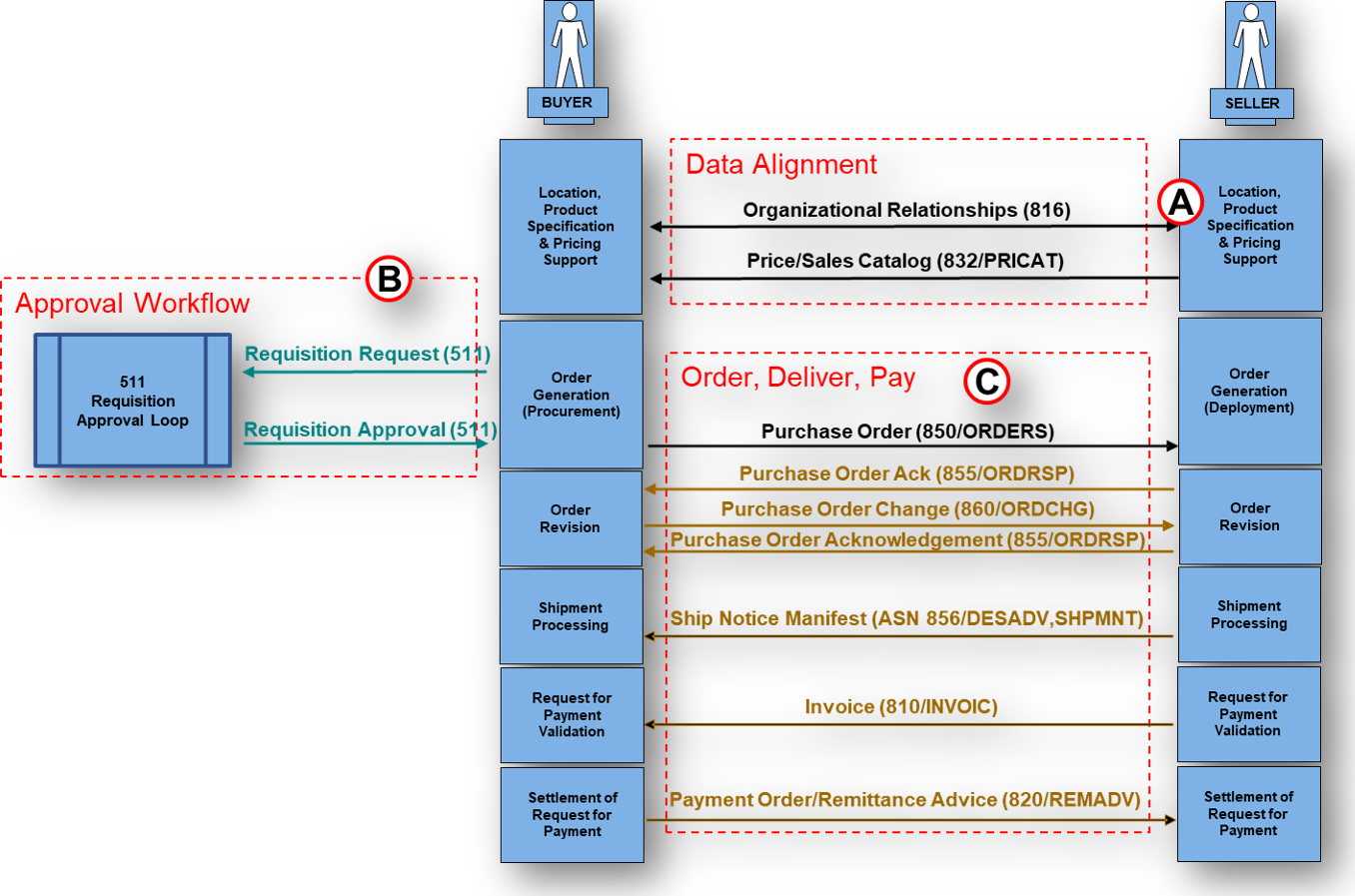
What is the EDI 832 – Price/Sales Catalog?
The EDI 832 Price/Sales Catalog transaction set supports the  electronic exchange of product catalog and pricing information between trading partners. The transaction replaces traditional paper catalogs by providing a structured, standardized method for communicating detailed product data and associated pricing across supply-chain networks using EDI. The EDI 832 message typically carries primary information in two parts: product identification and descriptive attributes, and pricing information tied to those products.
electronic exchange of product catalog and pricing information between trading partners. The transaction replaces traditional paper catalogs by providing a structured, standardized method for communicating detailed product data and associated pricing across supply-chain networks using EDI. The EDI 832 message typically carries primary information in two parts: product identification and descriptive attributes, and pricing information tied to those products.
Manufacturers, suppliers, distributors, retailers, and procurement platforms rely on the EDI 832 message to maintain synchronized product and pricing data across enterprise systems, eCommerce platforms, and downstream ordering processes.
How does PartnerLinQ use the EDI 832?
PartnerLinQ uses the EDI 832 to facilitate the accurate, timely,  and standardized exchange of product catalog and pricing information between trading partners. The 832 transaction enables suppliers to publish complete or partial catalogs while allowing buyers and distributors to consume structured data directly into ERP, procurement, and eCommerce systems.
and standardized exchange of product catalog and pricing information between trading partners. The 832 transaction enables suppliers to publish complete or partial catalogs while allowing buyers and distributors to consume structured data directly into ERP, procurement, and eCommerce systems.
PartnerLinQ implementations emphasize data consistency, automation, and system-to-system integration, reducing dependency on manual catalog updates and minimizing discrepancies across environments. Sellers commonly use the transaction to publish full catalogs, while selective updates support promotions, regional pricing, or item-level changes.
Catalog information exchanged is typically a (1) complete catalog or can arrive as (2) an incremental update carrying only updates and additions. An indication provided by the BCT10 Transaction Set Purpose Code, where the BCT10 qualifier would indicate an Original (‘00’) or an Addition (’02’) and may include information indicating 'Market Area', ‘Pricing Market’, ‘Zone’, or ‘Regional Pricing.’ in the header level REF segment. The mass exchanges of Price / Sales Catalog information can be made using the EDI 832 – Price/Sales Catalog, EDIFACT, and other globally recognized standards by way of Value Added Networks (VANs), FTP, MFTP, SFTP, AS2 and even API exchanges.
What responses to the EDI 832 Price / Sales Catalog are expected or sent?
While the EDI 832 does not mandate a functional business response transaction, trading partners often rely on functional acknowledgments, such as the EDI 997 or 999, to confirm syntactical receipt and compliance. Business-level acceptance, rejection, or pricing validation generally occurs downstream within procurement, merchandising, or master-data management workflows rather than through a dedicated response transaction. Pricing changes within procurement, merchandising, or master-data management workflows requiring updates of approvals as part of those workflows.
Functional Acknowledgements (997s) and message delivery notifications (MDNs) 
One of the stated benefits for using AS2 is the message delivery notification (MDN), although some may argue the MDN replaces the EDI 997 messages, the message delivery notification (MDN) used in AS2 only indicates the message has been received whereas the Functional Acknowledgement (997) the message has been received and confirms the delivery of information and documents any formatting errors or loss of data. Message Disposition Notifications (MDNs) and EDIFACT CONTRL are industry best practice, are automatically generated and sent by PartnerLinQ for transmission back to the sending party.
The 845 Price Authorization Acknowledgment
The 845 Price Authorization Acknowledgment business message can be used to accept, reject, or conditionally approve pricing proposed in a price-related transaction, the practice is commonly referred to as “Catalog Price Authorization. The 845 having also been described as ‘845 Pre-Order Price Validation’ or ‘845 Price Governance Acknowledgment’ within published documentation with trading partners treating the EDI 832 – Price/Sales Catalog as a proposed price event rather than an automatically accepted price.
Catalog Price Authorization Workflow
- Seller publishes EDI 832 containing new or revised pricing with item identifiers and/or qualifiers, effective dates, so-on.
- Buyer performs automated validation (price governance) responding with an EDI 845
- Accepts the catalog price as submitted
- Rejects the price (with reason codes)
- Conditionally approves (e.g., different effective date, subset of items, or revised price)
- Approved pricing becomes authoritative
Downstream transactions, that is transactions that follow the ‘845 Pre-Order Price Validation’ or ‘845 Price Governance Acknowledgment’ such as the EDI 850, 810, and chargeback documents including the 844 and 849, reference the authorized price set, typically identified by a ‘CT’ Contract Number in the REF in the EDI 832.
What does the EDI 832 Price / Sales Catalog support?
The EDI 832 supports structured communication of market relevant, partial or complete catalog and pricing data updates that enable automated updates across procurement, merchandising, and eCommerce systems. The 832 transaction also supports multiple market, packaging configurations, and currency requirements by way of AS2 and even API (Application Programming Interface) integrations.
What are the Key Features of the EDI 832?
The EDI 832 supports rich product identification, flexible pricing structures, standardized packaging descriptions, and multiple currencies. The 832 transaction accommodates extensive item detail using repeatable loops and standardized qualifiers while maintaining alignment with global identification systems such as GTINs, GLN, DUNs, UPCs, even UDI.
What is the Purpose of the EDI 832?
The purpose of the EDI 832 is to streamline catalog maintenance and the exchange of product and pricing information across trading partner networks. The 832 increases accuracy while it reduces manual data entry into procurement, merchandising, and eCommerce systems. The 832 improves data quality and supports scalable catalog management practices across partners, regions, and systems.
What Information is Included in the EDI 832?
The EDI 832 includes the following information categories:
| Information Category | Description |
|---|---|
| Item Identification | SKU, GTIN, UPC, vendor item numbers, and buyer item numbers |
| Product Description | Free-form descriptions and standardized product attributes |
| Packaging Details | Case pack, inner pack, weight, and dimensional data |
| Pricing Information | Base prices, discounts, and retail or landed cost indicators |
| Currency | ISO 4217 currency codes |
| Trading Party Identification | Buyer, seller, ship-from, and vendor identifiers |
What are the Essential Components of the EDI 832?
Essential Components of the EDI 832 include:
| Segment | Purpose |
|---|---|
| ST | Identifies the start of the transaction set |
| BCT | Establishes catalog purpose and identification |
| LIN | Identifies individual catalog items |
| PID | Provides item descriptions |
| CTP | Communicates pricing information |
| SE | Terminates the transaction set |
What are the Common Segments Included in the EDI 832?
Common Segments contained by the EDI 832 include:
| Segment | Business Function |
|---|---|
| REF | Reference identifiers such as market or vendor IDs |
| CUR | Currency specification |
| N1 | Trading partner identification |
| DTM | Date and time references |
| PO4 | Physical and packaging details |
| G55 | Consumer unit characteristics |
| CTT | Transaction totals |
Summary Table of Key Segments
| Segment | Loop | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ST | Header | Transaction control and identification |
| BCT | Header | Catalog purpose and identification |
| REF | Header/Detail | Market, vendor, or reference data |
| CUR | Header | Currency specification |
| N1 | Header | Party identification |
| LIN | Detail | Item identification |
| PID | Detail | Item description |
| PO4 | Detail | Packaging and physical details |
| G55 | Detail | Consumer unit characteristics |
| CTP | Detail | Pricing information |
| CTT | Summary | Line item totals |
| SE | Trailer | Transaction termination |
What Status Codes are used with the EDI 832?

While the EDI 832 does not define transaction-specific status codes, it does define an accurate, timely, and purpose-built data exchange by enabling suppliers to publish complete or partial catalogs to partners or markets. The EDI 832 does not mandate a status response or functional business response transaction, business status and handling occurs within the recipient’s internal systems and workflows rather than within the 832 itself or a prescribed response transaction. Functional acknowledgment transactions (997s) are generally used manage syntactical validation, and MDNs (Message Delivery Notifications) signal receipt when AS2 is engaged. Recipients can consume structured data adding it directly to ERP, procurement, and eCommerce systems.
What Reason Codes are used with the EDI 832?
The EDI 832 does not define standardized reason codes. Pricing exceptions, catalog changes, or item discontinuations are managed through updated catalog transmissions or internal governance processes.
What Use Cases does the EDI 832 Price / Sales Catalog support?
The EDI 832 supports a focused but very important set of product-master, pricing, and merchandising use cases across wholesale, retail, manufacturing, and distribution networks. Business-oriented use cases such as catalog publication, price updates, regional pricing & distribution, promotional pricing, and the synchronization of product master data, including pricing schemes across procurement, merchandising, and eCommerce platforms. Manufacturers use the 832 transaction to distribute authoritative product data, while buyers rely on it to maintain consistent pricing across locations and channels.
| Use Case | Primary Purpose | Common Business Scenarios | Key Information Communicated |
|---|---|---|---|
| Product Catalog Distribution | Share complete or partial product catalogs with trading partners | Manufacturer → Distributor item setup; Distributor → Retailer onboarding; Supplier → Marketplace enablement | Item identifiers (SKU, UPC, GTIN); descriptions; attributes; packaging hierarchy; UOMs |
| Price List Publication | Communicate standard, contract, or list pricing | Annual or quarterly price updates; MSRP and wholesale pricing; contract pricing distribution | Base price (CTP); price qualifiers; effective and expiration dates; allowances and charges |
| Item Setup & Maintenance | Maintain and update item master data | New item introductions; description changes; packaging or UOM updates; item discontinuations | Item status indicators (G53); revised descriptions; replacement or supersession references |
| Contract & Customer-Specific Pricing | Share negotiated pricing terms | Retailer-specific pricing; distributor tier pricing; regional price variations | Customer identifiers (REF); pricing qualifiers; quantity break pricing; validity periods (SAC/DTM) |
| Promotional & Temporary Pricing | Communicate time-bound pricing changes | Seasonal promotions; clearance pricing; limited-time discounts | Promotional price; start and end dates (DTM); promotion qualifiers |
| Pre-Order Enablement | Prepare partners to transact prior to availability | New product launches; future assortments; seasonal merchandise planning | Future effective dates (DTM); availability indicators; introductory pricing (SAC) |
| Data Synchronization Across Systems | Align product and pricing data across platforms | ERP ↔ Trading Partner sync; ERP ↔ Marketplace multi-sync; multi-channel consistency | Item master and pricing data used across downstream transactions |
What are the Benefits of the EDI 832?
The EDI 832 improves operational efficiency, enhances pricing accuracy, reduces manual data entry, and strengthens collaboration between and among trading partners. Automated – Price / Sales and catalog synchronization supports sales, faster item onboarding and a more reliable order to cash (procure to pay) processes.
Business Value Added
- Accelerates item onboarding and reduces manual item master setup
- Ensures pricing alignment before orders are placed
- Keeps ERP, WMS, OMS, and POS data synchronized
- Reduces pricing mismatches and invoice disputes
- Enables accurate promotional execution
- Supports forecasting, merchandising, and launch readiness
- Reduces downstream errors in 850s, 856s, and 810s
How efficient is the EDI 832?
The EDI 832 – Price/Sales Catalog achieves a high level of efficiency through standardized data structures, repeatable item loops, and automated system integration. The transaction is delivered as a ‘complete catalog’ or can arrive as an ‘incremental update’ carrying only updates and additions, an indication provided by the BCT10. When compared with transactions that require human intervention of any kind, the EDI 832 performs with much more efficiently than most reducing latency in catalog updates and minimizing errors introduced through manual maintenance.
How compliant is the EDI 832?
The EDI 832 adheres to ANSI X12 standards and supports alignment with GS1 identification frameworks. PartnerLinQ implementations leverage industry guidance and standardized delimiters to ensure interoperability and compliance across multiple industries.
What is the Format of the EDI 832?
The EDI 832 follows ANSI X12 formatting rules and is transmitted using standardized delimiters defined by PartnerLinQ. The structure includes header, detail, and summary sections, supporting multiple items and pricing records within a single transaction.
How accurate is the EDI 832?
The EDI 832 delivers remarkable high accuracy when integrated directly with source systems (systems of record) and automated (receipt) processing reduces transcription errors ensuring consistent pricing and product data across consuming systems and associated transactions.
What are the Limitations of the EDI 832?
The EDI 832 does not provide built-in business acknowledgments, acceptance, or dispute and resolution mechanisms. Governance, validation, and approval processes must be aligned between trading partners and handled externally within ERP, procurement, and eCommerce systems through supplemental transactions such as those listed below:
| Transaction | Role |
|---|---|
| MDN | Message Delivery Notification |
| 997 | Functional Acknowledgment |
| 845 | Price Authorization Acknowledgment (Response to the 832) |
| 810/880 | Invoice |
| 849 | Adjustment Response (Decision document) |
| 855 | Purchase Order Acknowledgment |
Are Guidelines and Sample Files available for the EDI 832?
Yes. PartnerLinQ provides sample EDI 832 – Price / Sales Catalog transaction and implementation guides through its Support and Guideline Management Team.
Sample EDI 832 implementation guides illustrate both inbound and outbound flows, segment layouts, and valid data examples and support testing and partner onboarding. Customized specification documents for use in on boarding and technical development are available upon request.
PartnerLinQ provides:
- EDI 832 Invoice transaction implementation guide
- Sample payloads
- Qualification and testing maps
- Error handling and best-practice notes
What are the Basic Questions for EDI Integration with the EDI 832?
Integration planning typically addresses transaction direction, trading partner scope, pricing governance, automation triggers, cross-reference management, and downstream system impacts. These considerations ensure scalable and maintainable catalog integration.
What Business-Level Workflow does the EDI 832 support?
The EDI 832 supports a catalog publication workflow in which suppliers publish authoritative product and pricing data, buyers ingest and validate that data, and downstream ordering systems consume the information during procure-to-pay processes.
Steps to get to approved/authoritative pricing does exist in some trade relationships. Achieved primarily through a ‘Catalog Price Authorization Workflow’ where the sender publishes an EDI 832 and the Buyer responds with an EDI 845 (after performing an automated validation, the process is seldom initiated between partners. The rationale for declining a ‘Catalog Price Authorization Workflow’ most often heard is, ‘Price disputes continue.’
What are the Best Practices for using the EDI 832?
Best practices emphasize automation, automation that begins with consistent and unique item identification alignment with GS1 standards (GTIN, GLN, Target Market) and controlled pricing governance. Regularly schedules catalog refresh cycles, and automated validation within both generating and consuming systems are also among the best practices cited as are a ‘Catalog Price Authorization’ process, one that support data integrity beginning with GS1 standards (GTIN, GLN, Target Market) and operational scalability for the best results.
What Transactions are associated with the EDI 832?
The EDI 832 is commonly associated with functional acknowledgments such as the EDI 997 or 999 and downstream ordering transactions including the such as the 845 Price Authorization Acknowledgment and the EDI 850 Purchase Order and EDI 810 Invoice.
| Transaction | Role |
|---|---|
| 810/880 | Invoice |
| 812 | Credit/debit memo (optional but common) |
| 820 | Remittance advice |
| 844 | Adjustment Request (Primary input to the 849) |
| 845 | Price Authorization Acknowledgment (Response to the 832) |
| 849 | Adjustment Response (Decision document) |
| 850 | Purchase Order |
| 855 | Purchase Order Acknowledgment |
| 856 | Advance Ship Notice |
| 860 | Purchase Order Change |
| 997 | Functional Acknowledgment |
Footnotes
- PartnerLinQ 832 v4010 Specification, Purpose and Overview, p.3
- PartnerLinQ 832 v4010 Specification, User Notes, p.3–4
- What is EDI 832, PartnerLinQ Overview
- PartnerLinQ 832 User Notes, Usage Context
- PartnerLinQ 832 Specification, Functional Handling
- PartnerLinQ 832 Specification, Segment Structure
- PartnerLinQ 832 LIN and CTP Segment Notes
- What is EDI 832, Purpose Section
- PartnerLinQ 832 User Notes, Data Content
- PartnerLinQ 832 Segment Summary Tables
- PartnerLinQ 832 Common Segment Usage
- PartnerLinQ 832 Functional Notes
- PartnerLinQ 832 Specification Commentary
- PartnerLinQ 832 Use Case Description
- PartnerLinQ 832 Benefits Overview
- PartnerLinQ 832 Automation Discussion
- PartnerLinQ 832 Compliance Notes
- PartnerLinQ 832 Delimiter and Format Notes
- PartnerLinQ 832 Accuracy Considerations
- PartnerLinQ 832 Limitations Commentary
- PartnerLinQ Support and Guidelines Notes
- PartnerLinQ Integration Questions
- PartnerLinQ 832 Workflow Description
- PartnerLinQ 832 Best Practices Guidance
- PartnerLinQ 832 Associated Transactions
Explore Our Integration Solutions
PartnerLinQ Integration Solutions
Connect Everything. Integrate Intelligently.
Future-Proof Your Business with Composable, AI Powered Connectivity.



