What is the EDI 849 Response to Product Transfer Account Adjustment?
The EDI 849 Response to P roduct Transfer Account Adjustment is an ANSI X12 transaction designed to communicate a manufacturer’s formal response to a distributor’s EDI 844 Product Transfer Account Adjustment claim.
roduct Transfer Account Adjustment is an ANSI X12 transaction designed to communicate a manufacturer’s formal response to a distributor’s EDI 844 Product Transfer Account Adjustment claim.
The EDI 849 enables the manufacturer to acknowledge, accept, adjust, or reject chargeback and contract-pricing claims submitted by wholesalers and distributors. The transaction serves as the reconciliation step in the contract-pricing chargeback process, ensuring that credits are assigned accurately based on eligible contract sales and validated contract data.
Within healthcare supply chains this transaction plays a central role in the contract administration life cycle where distributors—such as AmerisourceBergen, Cardinal Health, and others—submit chargeback claims seeking reimbursement from manufacturers for sales executed at contract prices. The EDI 849 ensures discrepancies are identified, clarified, and resolved while reducing manual reconciliation and expediting payment cycles.
How does PartnerLinQ use the EDI 849?
PartnerLinQ uses the EDI 849 to operationalize and standardize the reconciliation step between the manufacturer and the distributor. Manufacturers use PartnerLinQ to communicate whether a distributor’s 844 adjustment request is accepted as-is, accepted with adjustments, or denied—complete with reason codes, contract references, and item-level validation outcomes.
PartnerLinQ implements the EDI 849 in accordance with the Healthcare Distribution Alliance (HDA, formerly HDMA) guidelines and applies the enhancements, notes, and coding improvements reflected in the 2020 HDA implementation materials that supersede the earlier 2009 HDMA guidance.
PartnerLinQ uses the EDI 849 in the following manner:
- Confirms acceptance of undisputed contract sales.
- Communicates adjustments to quantities, pricing, or contract information.
- Identifies line-item errors requiring correction by the distributor.
- Supports enriched data elements, including contract identifiers, N1 location references, DEA and GLN codes, and item-level references.
- Carries HDA-endorsed reject reason codes via the AAA segment when the submitted contract number is incorrect, expired, or not yet in force.
- Generates 997 functional acknowledgments automatically upon receiving inbound 844s and sending outbound 849s.
This use of the EDI 849 provides a clean, high-integrity, and auditable reconciliation mechanism that removes manual intervention and accelerates the chargeback payment cycle.
What responses to the EDI 849 Response to Product Transfer Account Adjustment are expected or sent?
The  primary expected response to an 849 transmission is the 997 Functional Acknowledgment, which is used to indicate the results of a syntactical analysis of functional groups and their business messages and confirming the delivery of information and documents any formatting errors or loss of data.
primary expected response to an 849 transmission is the 997 Functional Acknowledgment, which is used to indicate the results of a syntactical analysis of functional groups and their business messages and confirming the delivery of information and documents any formatting errors or loss of data.
Functional Acknowledgments (997)
Functional Acknowledgment (997) are industry best practice should be sent back to PartnerLinQ on receipt of the Response to Product Transfer Account Adjustment (849) business message, the Functional Acknowledgment (997) response should be within 24 hours.
Functional Acknowledgment (997) are industry best practices and are automatically generated by PartnerLinQ for transmission back to the sending party whenever any transaction including the Product Transfer Account Adjustment (844) from the distributor
Business messages such as the EDI 849 Response to Product Transfer Account Adjustment with errors may be accepted with errors or rejected. Rejected messages must be corrected and re-transmitted by the sending party and should be returned within 24 hours.
Corrected 844 Product Transfer Account Adjustment submissions 
Responses to an 849 transmission may include a corrected 844 submissions from distributors whenever the 849 response identifies line items with resubmission behavior guided by AAA Request Validation segment reason codes, ensuring the necessary corrections occur or indicating adjusted or reconciled amounts through AMT, QTY, LIN, and PAD segments are needed.
What does the EDI 849 Response to Product Transfer Account Adjustment support?
The EDI 849 supports contract-pricing chargeback reconciliation providing full transparency into which items are accepted, which items require correction, and which items are denied. The EDI 849 Response contains details relating to and including:
- Validation of contract numbers (CON segment)
- Validation of contract status (CON03)
- Disputed item identification (AAA segment at detail level)
- Item-level adjustments (LIN, PAD, QTY, UIT, AMT)
- Original transaction linking (BRC and REF qualifiers)
- Identification of customer/ship-to locations (N1 loop)
- Reconciliation of credit amounts
- Dispute management and corrective workflows
What are the Key Features of the EDI 849 Account Adjustment Response?
Key features include: 
- Detailed or summary reconciliation capability, depending on trading partner agreements.
- Support for contract-specific validation, including reference, status, and timing rules.
- Line-item validation and rejection logic, driven by AAA03 and HDA reason code frameworks.
- Financial accuracy, providing explicit credit amounts, disputed adjustments, and total transaction amounts.
- Support for multiple location identifiers, including GLN, DUNS, HIN, DEA, SAN, and SCAC codes.
- Full auditability, enabling chargeback teams to trace disputes to contract terms.
- Compatibility with PartnerLinQ’s native connectivity framework, ensuring low-effort onboarding and consistent transformation logic.
What is the Purpose of the EDI 849?
The purpose of the EDI 849 is to formalize a manufacturer’s response to a distributor’s contract-pricing adjustment request accelerating the financial settlement process between partners by ensuring that contract-priced sales are validated and reimbursed accurately., providing:
- Adjusted credit amounts based on contract rules
- Clear identification of errors, such as invalid contract numbers or mismatched quantities
- Formal acceptance of valid chargebacks
- Rejected items with reason codes, enabling precise distributor correction
- Traceability between the original 844 and the reconciliation
What Information is Included in the EDI 849? 
The EDI 849 includes:
Header-Level Information
- Transaction purpose (BRC01)
- Processing date (BRC02)
- Reference numbers linking back to the 844 (BRC03/BRC04)
- Administrative notes (NTE)
- Additional references (REF segments)
Party Identification (N1 Loop)
- Manufacturer, distributor, or ship-to information
- Location codes (GLN, DUNS, DEA, SAN, HIN)
Detail-Level Information (CON Loop)
- Contract numbers (CON02)
- Contract status (CON03)
- Validation outcomes (AAA03)
- Item detail (LIN, PAD)
- Units, quantities, and amounts (UIT, QTY, AMT)
- Dates associated with adjustment activity (DTM)
Summary-Level Information
- Total number of contract line items (CTT01)
- Final transaction amount, if required (AMT)
What are the Essential Components of the EDI 849?
Essential components of the Response to Product Transfer Account Adjustment (849) reflect a structure compiled for accurate reconciliation, clear communication, and alignment with guidance. Each component providing for a specific business function that ensures the trading partners can accurately interpret contract line items, pricing, and adjustment logic.
| Essential Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Transaction Identification | The ST and BRC segments set the context for the response, linking the EDI 849 to the original 844 claim and identifying the purpose of the reconciliation. |
| Party Identification | N1 loops identify distributors, manufacturers, ship-to/customer locations, and administrative contacts using GLN, DUNS, HIN, DEA, SAN, and other identifiers. |
| Contract Validation | The CON segment carries contract numbers and statuses, ensuring that each product line ties back to a valid, active contract under which pricing was authorized. |
| Item-Level Response Detail | PAD, LIN, UIT, QTY, and AMT provide item identifiers, units, quantities, and associated credit amounts or adjustments. |
| Rejection and Validation Codes | AAA03 reason codes identify the exact cause of any rejection (e.g., incorrect contract number, contract expired, contract not yet in force). |
| Date References | DTM provides timestamps for adjustment activity, manufacturing details, eligibility windows, and response timelines. |
| Reconciled Totals | CTT and AMT segments summarize line counts, totals, and amounts that cannot be computed through other segments. |
| Audit Trail and References | REF segments at the header and detail levels carry cross-references, internal identifiers, and resubmission numbers for accurate traceability. |
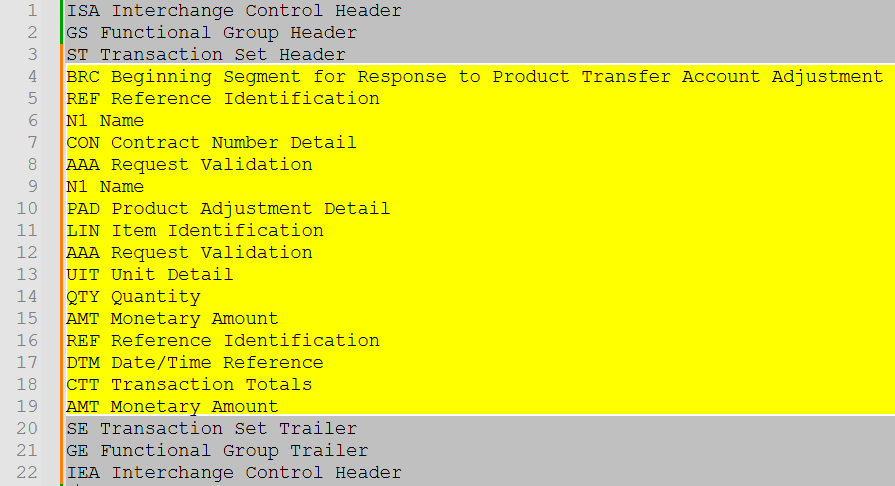
What are the Common Segments Included in the EDI 849?
According to the PartnerLinQ 849 specification (PartnerLinQ 849 v4010 20251121), the following segments appear in most EDI 849 implementations:
Header Segments
- ST – Transaction Set Header
- BRC – Beginning Segment for Response to Product Transfer Account Adjustment
- NTE – Notes/Special Instructions (optional)
- REF – Reference Identification
- N1 Loop – Name/Location identifiers (Distributor, Manufacturer, etc.)
Detail Segments (CON Loop)
- CON – Contract Number Detail
- AAA – Request Validation
- REF – Reference Identification (Detail-Level)
- N1 Loop – Customer or ship-to detail
Detail Segments (PAD Loop)
- PAD – Product Adjustment Detail
- LIN – Item Identification
- AAA – Request Validation (Item-Level)
- UIT – Unit Detail
- QTY – Quantity
- AMT – Monetary Amount
- REF – Reference Identification
- DTM – Date/Time Reference
Summary Segments
- CTT – Transaction Totals
- AMT – Total Monetary Amount (summary-level)
- SE – Transaction Set Trailer
| Segment | Purpose | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| ST | Identifies the transaction set and assigns a control number. | Required for every EDI document. |
| BRC | Establishes the purpose, processing date, and reference linkage to the 844. | Uses HDA codes for purpose. |
| REF | Carries reference identifiers at both header and detail levels. | Supports AM, CT, KL, RX, and other qualifiers. |
| N1 Loop | Identifies key trading partners, ship-to customers, and administrative entities. | Supports GLN, DUNS, HIN, DEA, SAN, SCAC. |
| CON | Identifies the contract number and status. | CON03 uses VA; rejections appear in AAA03. |
| AAA | Communicates acceptance or rejection reason codes. | BB, CC, DD used for contract-level failures. |
| LIN | Identifies product items, GTINs, SKUs, NDCs, etc. | Supports multiple item qualifiers. |
| PAD | Provides product adjustment detail. | Ties to LIN for pricing and quantity validation. |
| UIT | Specifies units of measure. | Optional depending on trading partner use. |
| QTY | Provides relevant quantities such as billed, eligible, or credited. | Required in item-level validation. |
| AMT | Provides monetary values for credit, adjustments, or totals. | Used only when amount cannot be computed elsewhere. |
| DTM | Supplies timestamps for eligibility, transaction dates, or contract durations. | Used widely for contract enforcement. |
| CTT | Summarizes line counts and totals. | Required. |
| SE | Ends the transaction set. | Required. |
What Status Codes are used with the EDI 849?
| Segment | Purpose | Code Set |
|---|---|---|
| AAA01 | Indicates Yes/No outcome | Typically N (No) for rejections |
| AAA02 | Agency assigning code values | Frequently DR (National Wholesale Druggists Association) |
| AAA03 | Reject Reason Code | More than 30 rejection qualifiers appear in most EDI 849 implementations, many HDA-endorsed and typical from a pool of more than 200. |
The EDI 849 uses status codes—principally within the AAA Request Validation segment—to convey acceptance or rejection outcomes at both the contract and item levels.
Contract-Level Status Codes (AAA03)
- BB – Contract Number Incorrect
- CC – Contract Has Expired
- DD – Contract Not Yet in Force
Additional Item-Level Status Indicators
Depending on trading partner agreements, typically aligned these to HDA’s broader guidance and appearing in most EDI 849 implementations to maintain industry-compliant reconciliation behavior item-level AAA03 may reflect:
- Incorrect item number (14)
- Missing Sale or Inventory position (A1, A5)
- Contract Number Incorrect (BB)
- Ineligible Customer (FF, GG, HH, II, JJ…)
- Ineligible Item or item found on contract (KK)
- Unit Cost Missing or Incorrect (UU)
- Ineligible sale date (MM)
What Reason Codes are used with the EDI 849?
Aligned these to HDA’s broader guidance and appearing in most EDI 849 implementations Reason codes are essential because they guide distributors in correcting and resubmitting 844 claims with errors through automated detection.
Reason Codes Samples:
| Code | Meaning | Usage Notes |
|---|---|---|
| BB | Contract Number Incorrect | Contract not recognized or mismatched |
| CC | Contract Has Expired | Contract term has ended |
| DD | Contract Not Yet In Force | Contract start date not yet reached |
What Use Cases does the EDI 849 support?
The EDI 849 supports multiple business scenarios central to healthcare contract administration:
Primary Use Cases
- Chargeback Reconciliation: Manufacturer accepts or disputes distributor-submitted adjustments.
- Exception Management: Communicates item-level and contract-level discrepancies.
- Financial Settlement Acceleration: Supports faster reimbursement cycles for contract-priced sales.
- Audit and Compliance: Offers a structured, machine-readable record of acceptance, adjustment, or denial.
- Multi-Contract Environments: Clarifies which contract applies when multiple agreements overlap.
What are the Benefits of the EDI 849 Response to Product Transfer Account Adjustment?
The EDI 849 delivers measurable operational and financial advantages:
- Enhanced auditability, providing a clear historical trail at the line-item level.
- Faster chargeback resolution, cutting down on phone calls, emails, and PDFs.
- Greater data accuracy through standardized contract, item, and location identifiers.
- Higher trading partner satisfaction, reducing back-and-forth and ambiguity.
- Lower cost-to-serve, especially when combined with PartnerLinQ’s unified connectivity model.
- Reduced manual reviews by providing structured, machine-readable reconciliation.
How efficient is the EDI 849?
The EDI 849 streamlines chargeback reconciliation by:
- Eliminating manual data entry.
- Enforcing consistent validation rules (AAA logic).
- Ensuring accurate, system-driven contract matching.
- Delivering immediate visibility into rejected items.
- Reducing cycle times from days/weeks to hours.
PartnerLinQ increases efficiency further with automatic 997 acknowledgments, reusable transformation components, and integration accelerators like reporting and alerting built into its connectivity platform.
How Compliant is the EDI 849?

PartnerLinQ’s EDI 849 Response to Product Transfer Account Adjustment complies with ANSI X12 version 4010 standards and the platform supports interchange via AS2, VAN, and REST API transport methods. PartnerLinQ’s guidelines reinforce compliance efforts and promote consistency across trading partners. Compliance is ensured and maintained through adherence to control segments, industry-standard qualifiers (GLN, D-U-N-S, etc.), secure message validation protocols including 997, 999, and MDN acknowledgments and global frameworks like ISO 3166-1 country codes and GS1 data structures for multi-region data exchange.
- Adherence to ANSI X12 version 4010 standards, as reflected in PartnerLinQ’s specification
- Alignment with HDA standards, which supersede HDMA guidance (2009 → 2020).
- Through thoughtful, structured, and consistent methodologies that downstream chargeback systems can reliably interpret and respond to
- Use of proper reject reason codes (BB, CC, DD)
- Use of correct identifiers (GLN, DUNS, DEA, HIN).
What is the Format of the EDI 849?
The EDI 849 adheres to the ANSI X12 v4010 format, following a structured hierarchy:
- Header Segments (ST, BRC, REF, N1)
- Detail Segments
- CON Loop
- PAD Loop
- Summary Segments (CTT, AMT, SE)
Separators follow PartnerLinQ production delimiter standards:
- Segment: hex 15 or ~
- Element: | or *
- Sub-element: >
How Accurate is the EDI 849?
Accuracy  as with most transaction-based implementations is largely dependent on synchronized data; including master data, entity identifiers, location codes, partner code lists, even external lists line DEA and Contract numbers and is achieved through the availability of details at the enterprise level and automated validation rules embedded in PartnerLinQ’s integration layer. Validation of ST/SE control numbers and mandatory content supports processing integrity as each 849 is cross-checked against existing records to detect duplicates and an assortment of errors. PartnerLinQ also performs validations on EDI 849 Response transactions driving accuracy through:
as with most transaction-based implementations is largely dependent on synchronized data; including master data, entity identifiers, location codes, partner code lists, even external lists line DEA and Contract numbers and is achieved through the availability of details at the enterprise level and automated validation rules embedded in PartnerLinQ’s integration layer. Validation of ST/SE control numbers and mandatory content supports processing integrity as each 849 is cross-checked against existing records to detect duplicates and an assortment of errors. PartnerLinQ also performs validations on EDI 849 Response transactions driving accuracy through:
- Validation of each claim line against contract master data.
- Clear identification of discrepancies at both contract and item levels.
- Inclusion of corrected reference information in REF segments.
- Enforcement of date accuracy through DTM segments.
- System-enforced consistency when using PartnerLinQ’s integration layer.
This ensures that financial credits issued to distributors precisely reflect contractual obligations.
What are the Limitations of the EDI 849?
While highly effective, the EDI 849 does have some structural limitations, constraints that are typical across ANSI X12 documents.
- The EDI 849 does not do well with unstructured data or large data sets (e.g., attached documents).
- NTE notes are non-processable, reducing automation when used improperly
- AMT segments must be used sparingly, only when amounts cannot be computed.
- Dependent on accuracy of the inbound 844, garbage-in/garbage-out remains a risk.
- Contract eligibility logic is generally external which makes the EDI 849 dependent on external data cached from other systems (e.g., ERP, pricing, or chargeback systems).
Are Guidelines and Sample Files for the EDI 816 Available?
Yes. PartnerLinQ provides sample EDI 849 Response to Product Transfer Account Adjustment Transaction and implementation guides through its Support and Guideline Management Team.
Sample EDI 849 implementation guides illustrate both inbound and outbound flows, segment layouts, and valid data examples and support testing and partner onboarding. Customized specification documents for use in on boarding and technical development are available upon request.
PartnerLinQ provides:
- EDI 849 Response to Product Transfer Account Adjustment transaction implementation guide
- Sample payloads
- Qualification and testing maps
- Error handling and best-practice notes
What are the Basic Questions for EDI Integration with the EDI 849?
Basic Questions for EDI Integration ensure a consistent and predictable onboarding experience, here are some questions to look at leading up to analysis, before decision making, and certainly before EDI integration
- Are there Samples and Specs available?
- What is the general direction of the transaction?
- Are they Inbound to the client or Outbound from the client to another party?
- Are there more than one party involved in exchanging the EDI 849 response transaction?
- Are there other interested parties?
- What transactions might these interested parties be a party to?
- What response to the transaction is expected or sent?
- Is a response to the transaction a timed event?
- Are business rule notifications involved/needed for the local team?
- Are there samples and specs of the response transaction available?
- How are changes to the EDI 849 response managed today?
- Is there a workflow?
- Is there automation? (an enterprise or internal system trigger) or are EDI 849 business message transactions triggered manually?
- Are responses and changes automatically triggered? (an enterprise or internal system trigger) or do transactions require human intervention?
- Have wholesaler identifiers been captured?
- Have Contract numbers, beginning and ending dates been captured from the enterprise or data storage?
- Have document numbers and dates been captured from the 844?
- Have adjustment types and amounts been captured?
- Have product-level details been mapped?
- What about inventories?
- Has acceptance/rejection logic been captured?
- Have reconciliation details been approved for transmission?
What Business Level Workflow does the EDI 849 support?
The  849 supports the classic 844 - 845 - 849 chargeback reconciliation cycle automating each of these touchpoints, reducing friction and increasing settlement velocity.
849 supports the classic 844 - 845 - 849 chargeback reconciliation cycle automating each of these touchpoints, reducing friction and increasing settlement velocity.
- Distributor sells product at contract price.
- Distributor submits EDI 844 to manufacturer requesting reimbursement.
- Manufacturer acknowledges receipt of the transaction (e.g., 997, 999, MDN)
- Manufacturer validates/investigates claim against contract agreements.
- Manufacturer sends EDI 849 indicating:
- Acceptance
- Adjustment
- Denial (with AAA03 reason codes)
- Distributor corrects errors, if any.
- Corrected 844 is resubmitted, when applicable.
- Manufacturer processes credits and finalizes reimbursement.
What are the Best Practices for using the EDI 849?
- Treat the EDI 849 as a Formal Financial Record - Ensure data is validated against internal ERP, WMS, and finance systems before transmission.
- Align the 849 Directly With the 844 Case or Adjustment Request - reference the original document number, case ID, or adjustment request.
- Consistency is Key – Use consistent Status and Reason Codes - Standardize codes across departments (Finance, Customer Service, Compliance, Supply Chain) and avoid “miscellaneous” or catch-all reason codes—they undermine accountability.
- Ensure Completeness – by cross-reference supporting data (e.g., REF01.REF02) this includes invoices, PODs, returns, pricing files, contracts, and ensure all item identifiers (SKU, UPC, GTIN, supplier item ID) match.
- Maintain Synchronization Across Systems (ERP, WMS, Finance) - Reconcile item, price, and allowance master data between partners regularly, and before engaging 844, 845, 849 processing.
- Provide Line-Item Details - Break out all items individually—never summarize a claim, claims can be complex.
- Maintain a Rejection Log - Align rejection logic with contractual terms and published policies, maintain FAQs/playbooks for common acceptance/rejection scenarios and map each rejection to a precise code - include a narrative explanation when appropriate to do so.
- Create, abide, and track SLAs - Use automation (e.g., PartnerLinQ’s workflow engines) to reduce manual processing time. Respond to 844 or adjustment requests as quickly as possible—delays create cash-flow issues. Monitor late or aging adjustment cases and escalate exceptions.
- Validate Pricing, Allowances, and Promotion Rules Before Finalizing - Confirm pricing against contracts, catalogs, pricing files, promotions, rebates, incentives, and allowances and ensure correct GL mapping for all accepted credits or debits
- Close the Loop - the EDI 849 is often the final step in the dispute lifecycle, provide complete acceptance/rejection detail in the 849, avoid “attachments”., align the 849 with a financial post, communication by way of a precise 849 accelerates settlements and improves cash flows.
What Transactions are associated with the EDI 849?
| Transaction | Role in the 849 Lifecycle |
|---|---|
| EDI 810 / 880 | Invoice validation source |
| EDI 812 | Final credit/debit memo (optional but common) |
| EDI 820 | Downstream remittance tied to accepted adjustments |
| EDI 832 | Price file / contract validation reference |
| EDI 844 | Adjustment Request (Primary input to the 849) |
| EDI 845 | Price Authorization Acknowledgment (Response to the 832) |
| EDI 849 | Adjustment Response (Decision document) |
| EDI 856 | Shipping evidence used in dispute review |
| EDI 997 / 999 | Transmission and compliance acknowledgment |
Explore Our Integration Solutions
PartnerLinQ Integration Solutions
Connect Everything. Integrate Intelligently.
Future-Proof Your Business with Composable, AI Powered Connectivity.



