What is the EDI 810 Invoice transaction?
The EDI 810 Invoice transaction is a standardized A NSI X12 electronic document used for business-to-business (B2B) communications to communicate billing information for goods and services between trading partners. Its primary purpose is to allow businesses to electronically transmit detailed invoice information for goods or services rendered to their trading partner counterparts, counterparts such as suppliers, vendors, clients, customers, or retailers. Organizations transmit a complete EDI 810 Invoice transaction, a machine-readable invoice that drives automated posting, cash application, and reconciliation.This electronic process enables automated billing, payment processing, and reconciliation while minimizing paperwork and human error. Operations teams gain speed and accuracy because the document eliminates rekeying and reduces exception rates.
NSI X12 electronic document used for business-to-business (B2B) communications to communicate billing information for goods and services between trading partners. Its primary purpose is to allow businesses to electronically transmit detailed invoice information for goods or services rendered to their trading partner counterparts, counterparts such as suppliers, vendors, clients, customers, or retailers. Organizations transmit a complete EDI 810 Invoice transaction, a machine-readable invoice that drives automated posting, cash application, and reconciliation.This electronic process enables automated billing, payment processing, and reconciliation while minimizing paperwork and human error. Operations teams gain speed and accuracy because the document eliminates rekeying and reduces exception rates.
How does PartnerLinQ use the EDI 810 Invoice transaction?
PartnerLinQ employs the 810 Invoice transaction set to streamline billing processes for products and services.
employs the 810 Invoice transaction set to streamline billing processes for products and services.
The 810 message is generated by suppliers after shipment confirmation and aligns the message to purchase order and receipt records for three-way matching. The result is a electronic bill to buyers for goods and services provided. The transaction allows buyers to record payment requests and update their financial systems automatically, facilitating a seamless flow from purchase order to payment. Finance teams receive clean header and line data that post directly to accounts payable. Stakeholders investigate disputes using narrative and coded references carried in BIG, REF, and SAC segments, which shortens resolution cycle and the data transmitted within the 810 message supports automated cross-referencing between purchase orders, shipping notices, and receipt confirmations, reducing the need for manual intervention and improving accuracy across the Order-to-Cash process.
What responses to the EDI 810 Invoice transaction are expected/sent?
Typical receivers return a 997 or 999 functional acknowledgment for syntax acceptance. Accounts payable may issue an 824 Application Advice when business rules fail. Treasury closes the cycle with an 820 Payment Order/Remittance Advice to communicate settlement details.
Functional Acknowledgements (997s) and message delivery notifications (MDNs) 
One of the stated benefits for using AS2 is the message delivery notification (MDN), although some may argue the MDN replaces the EDI 997 messages, the message delivery notification (MDN) used in AS2 only indicates the message has been received whereas the Functional Acknowledgement (997) the message has been received and confirms the delivery of information and documents any formatting errors or loss of data. Message Disposition Notifications (MDNs) and EDIFACT CONTRL are industry best practice, are automatically generated and sent by PartnerLinQ for transmission back to the sending party.
How do we support the EDI 810 Invoice transaction?
Order-to-cash flow reaches completion when the 810 posts and settles. Sellers reference the purchase order number and date in BIG04 and BIG03. Item lines in IT1 carry quantities, units, prices, and product identifiers, while SAC communicates allowances and charges at header or line level. Buyers reconcile totals in TDS and taxes in TXI before authorizing payment.
What are the Key Features of the EDI 810 Invoice transaction?
- Structured header and detail sections support fast posting and clear audit trails.
- Robust reference handling links invoices to orders, shipments, and contracts.
- Header- and line-level adjustments enable precise pricing and chargeback control.
- Multi-currency and tax elements support cross-border operations at scale
What is the Purpose of the EDI 810 Invoice transaction?
Commercial exchanges conclude through an official request for payment delivered by the 810. Finance teams rely on unambiguous line-level pricing and totals that support timely settlement and accurate financial reporting.
What Information Included in the EDI 810 Invoice transaction? 
An EDI 810 Invoice mirrors the structure and content of a paper invoice but in a digital, standardized form. Each invoice includes key details such as:
- Invoice number and issue date
- Buyer, Seller, and Remittance party identification (Factors)
- Purchase order references and remit-to details
- Order details (quantities, unit prices, item identifiers)
- Allowances, discounts, or service charges
- Tax information, and monetary totals
- Total amount due, payment terms, and tax details where applicable
Summary Table of Key Segments
| Segment | Name | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| ST | Transaction Set Header | Begins and controls the set |
| BIG | Beginning Segment for Invoice | Identifies invoice and PO |
| CUR | Currency | Defines currency context |
| REF | Reference Identification | Transmits contextual IDs |
| N1/N2/N3/N4 | Party/Address | Identifies legal and physical parties |
| DTM | Date/Time Reference | Adds relevant dates/times |
| IT1 | Baseline Item Data | Defines each invoice line |
| QTY | Quantity | Adds supplemental quantities |
| IT3 | Additional Item Data | Supplies alternate UOM/attributes |
| PID | Product/Item Description | Adds readable descriptions |
| SAC | Allowances/Charges | Shows discounts/fees |
| TDS | Total Monetary Value | Summarizes amounts due |
| TXI | Tax Information | Specifies tax rates/amounts |
| CTT | Transaction Totals | Counts lines and hashes |
| SE | Transaction Set Trailer | Closes and confirms counts |
What are the Essential Components of the EDI 810 Invoice transaction?
The essential components of the 810 Invoice include segment structures that define how billing information is exchanged between trading partners. Each segment below summarizes the key element(s) and PartnerLinQ-specific interpretation.
- ST – Transaction Set Header: Indicates the start of the transaction set and assignsa control number. PartnerLinQ requires unique transaction set control numbers that increment sequentially within each functional group. This ensures traceability and message integrity.
- BIG – Beginning Segment for Invoice: Specifies the invoice issue date, invoice number, purchase order date, and purchase order number. PartnerLinQ typically aligns each invoice to a single shipment, with consolidation practices varying by partner relationship.
- CUR – Currency: Specifies the transaction currency using ISO 4217 three-letter codes such as USD, CAD, or GBP. PartnerLinQ adheres to international standards for currency exchange representation.
- REF – Reference Identification: Provides auxiliary reference data between trading partners such as Bill of Lading (BM), Purchase Order (PO), or Customer Reference (CR) numbers. These identifiers aid in reconciliation and contextual processing of the invoice data.
- N1/N3/N4 – Name and Address Loops: Identifies entities involved in the transaction including buyer, seller, ship-to, and remit-to parties. PartnerLinQ supports the D-U-N-S (01), GLN (UL), and SAN (15) identification codes for global traceability.
- IT1 – Baseline Item Data: Provides detailed line-item billing information including item number, quantity, unit of measure, and unit price. PartnerLinQ ensures item-level consistency between the purchase order (850), advance ship notice (856), and invoice (810).
- TDS – Total Monetary Value Summary: Summarizes the total monetary amount of the invoice including all line items, taxes, and adjustments. Used for validation of invoice total accuracy before transmission.
What are the Common Segments Included in the EDI 810 Invoice transaction?
Operational implementations typically include ST, BIG, REF, N1/N2/N3/N4, IT1, SAC, TDS, and SE. Many partners also require CUR, DTM, QTY, IT3, PID, and TXI to support pricing, taxation, and item clarity.
The 810 Invoice uses the BIG Beginning Segment for the Invoice (810) message to indicate the beginning of an invoice transaction and does not typically carry a status code, though some are present in the BIG09 Action Code, they are seldom used.
Invoice Lifecycle is a practical matter and a practice within some supply chain relationships. Invoice Status in terms of state and business process usually includes Open, Approved, Paid, Short-Paid, and Disputed.
Electronic acknowledgments communicated by way of 997, and 999 add Accepted and Rejected outcomes of an EDI 810 transmission. Where Functional Acknowledgments (997s) and Implementation Acknowledgments (999s) are automatically generated by EDI translation software for transmission back to the sending party, the Application Advice (824) business message is often generated by downstream data processing systems, eliminating the need to communicate application errors by phone, fax, or mailed paper reports. It allows the originator of the transaction to correct inconsistencies in a timely manner, minimizing the impact on time sensitive applications.
What Reason Codes are used with the EDI 810 Invoice transaction?
Reason codes though accommodated within the X12 EDI 810 standard are not typically used. Common reasons for invoice variances include Price Differences, Quantity Discrepancies, Freight Variance, Tax Exception, and Missing Reference. Structured financial adjustments are generally communicated within the SAC segment (Service, Promotion, Allowance, or Charge Information) while content issues that arise can be managed with the help of the 824 Application Advice.
What Reason Codes are used with the EDI 810 Invoice transaction?
Reason codes though accommodated within the X12 EDI 810 standard are not typically used. Common reasons for invoice variances include Price Differences, Quantity Discrepancies, Freight Variance, Tax Exception, and Missing Reference. Structured financial adjustments are generally communicated within the SAC segment (Service, Promotion, Allowance, or Charge Information) while content issues that arise can be managed with the help of the 824 Application Advice.
What Use Cases does the EDI 810 Invoice transaction support?
Common use cases for the 810 Invoice include supplier billing for shipped goods, service invoicing, freight, and promotional charge reconciliation.
- Suppliers invoice for goods and services tied to a purchase order and receipt in a process known as 3 way match.
- Service providers bill contract deliverables or time-and-materials with descriptive content carried in the PID.
- Carriers may invoice freight where accessorial surcharges appear in the SAC segment in some circumstances for example where shippers have not integrated the EDI 210 invoice.
What are the Benefits of the EDI 810 Invoice transaction?
Benefits include faster payment cycles, automated reconciliation, reduced errors, and improved compliance
- Faster posting accelerates cash conversion and lowers days sales outstanding (DSO)
- Lower error rates reduce rework and improve partner satisfaction.
- Line-level structure raises audibility and compliance readiness.
How efficient is the EDI 810 Invoice transaction?
Straight-through processing routes clean transactions automatically and isolates true exceptions for review.
How Compliant is the EDI 810 Invoice transaction?
Adherence to X12 and ISO/GS1 conventions increases interoperability and reduces onboarding time.
What is the Format of the EDI 810 Invoice transaction?
Version 4010 organizes the 810 into heading, detail, and summary sections with loops, qualifiers, and code lists.
How Accurate is the EDI 810 Invoice transaction?
Consistent identifiers, unit measures, and tax calculations ensure totals reconcile across order, shipment, and invoice records.
What are the Limitations of the EDI 810 Invoice transaction?
A Free-form NTE notes segment provide flexibility yet reduces machine process-ability. Avoid them unless specifically required to use them.
Are Guidelines & Sample Files for the EDI 810 Invoice transaction?
Yes. PartnerLinQ provides sample EDI 810 Invoice transaction and implementation guides through its Support and Guideline Management Team. Sample EDI 810 implementation guides illustrate both inbound and outbound flows, segment layouts, and valid data examples and support testing and partner onboarding. Customized specification documents for use in on boarding and technical development are available upon request.
PartnerLinQ provides:
- EDI 810 Invoice transaction transaction implementation guide.
- Sample payloads.
- Qualification and testing maps.
- Error handling and best-practice notes.
What are the Basic Questions for EDI Integration with the EDI 810 Invoice transaction?
When integrating the 810 Invoice transaction, key questions include:
- Is the transaction inbound or outbound relative to the ERP?
- Are there Samples and Specs available?
- What is the general direction of the transaction?
- Are there other interested parties?
- What transactions might these interested parties be a party to?
- What response(s) to the transaction are expected or sent
- What payment terms and currency details are required?
- Are Service, Allowance, or Charge (SAC) segments expected?
- What about taxes? (TXI)
- What system triggers the 810 – manual or automated?
- Is there automation? (an internal systems trigger) or are Invoice (810) business message transactions triggered manually?
- How are invoice updates or changes handled?Are responses and changes automatically triggered? (an internal systems trigger) or do transactions require human intervention?
- What about terms of payment that come from inbound orders, how will those be accommodated/validated?
What Business Level Workflow does the EDI 810 Invoice transaction support?
- Seller ships goods and posts shipment confirmation.
- Seller issues 810 with PO and shipment context.
- Buyer returns 997/999 functional acknowledgment.
- Buyer performs three-way match.
- Buyer sends 824 Application Advice if issues arise.
- Buyer settles invoice and sends 820.
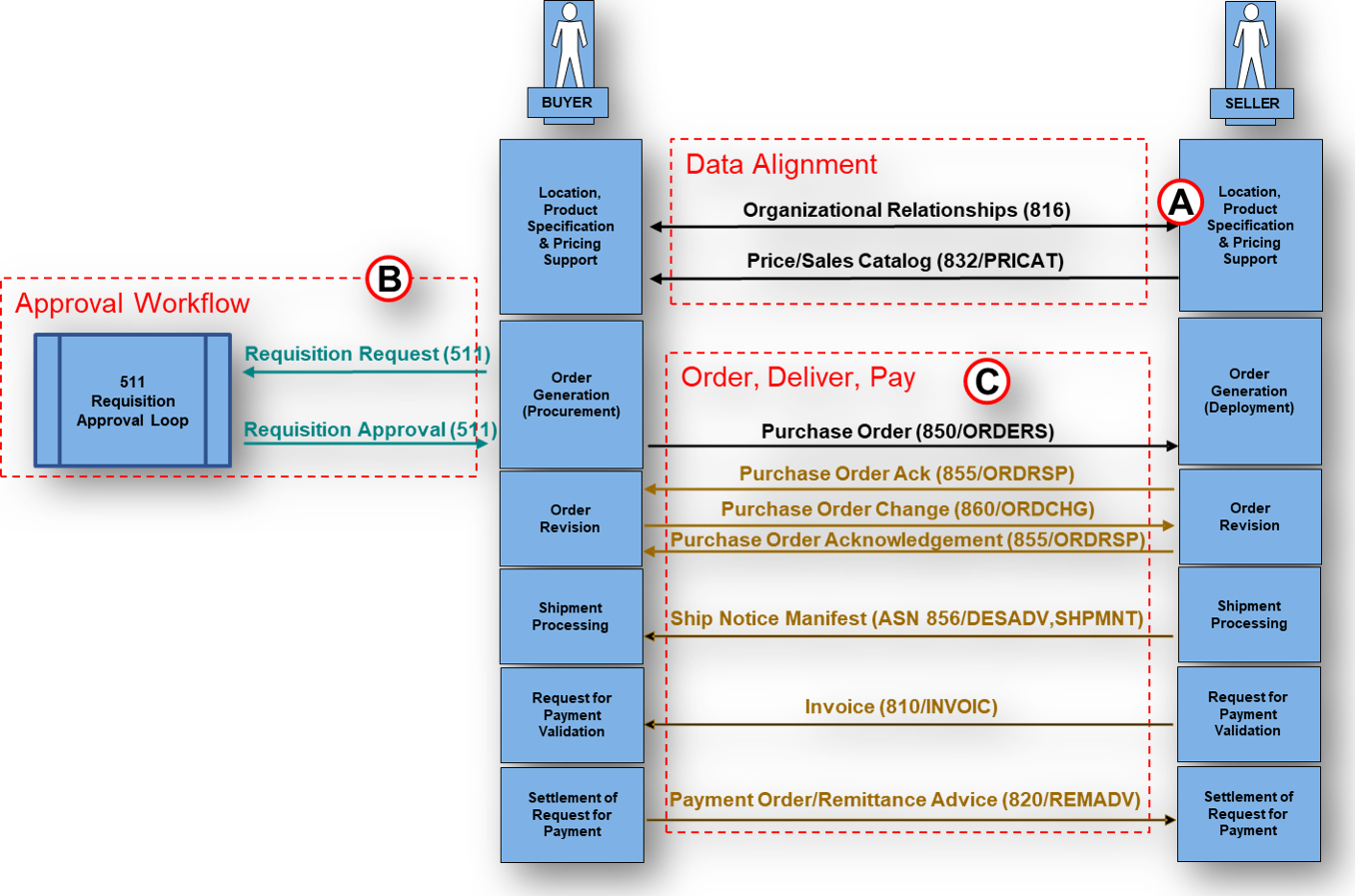
What are the Best Practices for using the EDI 810 Invoice transaction?
- Teams maintain strict ST02/SE02 control sequencing and verify SE01 counts before transmission.
- Implementations centralize code lists for qualifiers, UOM, taxes, and SAC codes to prevent drift.
- Mappings enforce consistent identifiers across 850, 856, and 810 documents for clean matching.
What Transactions are associated with the EDI 810 Invoice transaction?
- 850 - Purchase Order - Originates commercial terms referenced by the invoice.
- 855 - PO Acknowledgment - Communicates acceptance or changes that affect billing.
- 856 - Advance Ship Notice - Provides shipment detail used for matching and freight logic.
- 860 - PO Change - Issues updates that can require invoice correction.
- 824 - Application Advice - Reports content or business rule exceptions.
- 997/999 - Functional Acknowledgment - Confirms syntactic acceptance or rejection.
- 820 - Payment/Remittance - Delivers settlement details that close the transaction.



