What is the EDI 820 Payment Order/Remittance Advice? 
The EDI 820 Payment Order/Remittance Advice is an ANSI X12 financial transaction used to communicate payment details between trading partners, including settlement amounts, referenced invoices, adjustment values, banking information, and remittance alignment expectations. The 820 transaction communicates the payer’s intent to settle one or more financial obligations with the payee and is used alongside checks and electronic funds transfer (EFT) mechanisms such as ACH, wire, or other automated transfer/payment options/methods.
Businesses use the EDI 820 to provide payment execution details and advisory information, including invoice references, amounts paid, and adjustments applied. The transaction functions as the structured replacement for paper checks and remittance coupons, and for unstructured email statements or advise. The EDI 820 may serve solely as a communication instrument (remittance advice) or operate in concert with automation, banking systems (e.g., cash application, lock box, BPO) to initiate settlement instructions (payment order) or make cash application.
The Payment Order/Remittance Advice supports domestic and international payments, multiple invoices per remittance, rebate recovery, promotional offsets, and settlement reconciliation workflows. The data structure supports both traceability of payments and reconciliation activities, allowing both parties to align detailed ledger entries and support downstream financial reporting processes with relative ease.
How does PartnerLinQ use the EDI 820 Payment Order/Remittance Advice?
PartnerLinQ uses the EDI 820 to communicate structured remittance and payment settlement information between payers and payees. The 820 typically transaction notifies the seller of pending or completed payment allocations and provides supporting detail necessary to reconcile the invoice, invoiced amounts, adjustments, allowances, credits, and deductions.
PartnerLinQ supports both operational modes of the 820:
- Remittance Only: The transaction accompanies or precedes payment and provides structured financial information used for revenue posting and reconciliation.
- Payment + Remittance: The 820 drives the transfer of funds and provides the supporting ledger detail for accounting and cash application.
 PartnerLinQ enables the payer to bundle supporting remittance information with the payment or transmit the remittance as a separate message in either case and particularly when separate transmission occurs, PartnerLinQ supports match-linking through the TRN (Trace) segment to reconcile the EFT transaction with the corresponding advice.
PartnerLinQ enables the payer to bundle supporting remittance information with the payment or transmit the remittance as a separate message in either case and particularly when separate transmission occurs, PartnerLinQ supports match-linking through the TRN (Trace) segment to reconcile the EFT transaction with the corresponding advice.
PartnerLinQ also supports bank-originated 820 message receipt for cash application scenarios, including environments where the bank does not transform files for partner consumption. In these cases, the file is processed and either rendered into an 820 message and ingested or rendered into a structure suited more toward human consumption and reconciliation.
The PartnerLinQ platform ensures the alignment of the 820 with other financial and supply chain transactions including EDI 810 (Invoice), EDI 824 (Application Advice) and EDI 812 (Credit/Debit Adjustment). Automated posting rules can be applied based on remittance detail, tolerance thresholds, partner configurations, and defined reconciliation rules.
What responses to the EDI 820 Payment Order/Remittance Advice are expected or sent?
 Responses to the EDI 820 depend on whether the transaction is being used solely for remittance detail or paired with bank-initiated or system-initiated settlement instructions. Functional acknowledgments, including the 997 and the 999 Implementation Acknowledgment, confirm receipt and syntax validation and may appear as part of standard confirmation workflows.
Responses to the EDI 820 depend on whether the transaction is being used solely for remittance detail or paired with bank-initiated or system-initiated settlement instructions. Functional acknowledgments, including the 997 and the 999 Implementation Acknowledgment, confirm receipt and syntax validation and may appear as part of standard confirmation workflows.
Some implementations generate an 824 Application Advice when a remittance file contains process-level issues requiring correction or business-level exceptions requiring review. When discrepancies exist—such as unexpected deductions, unresolved dispute codes, or unmatched invoice references—reconciliation may trigger follow-up communication or processing in the form of an EDI 812 Credit/Debit Adjustment.
PartnerLinQ recommends the use of automated reconciliation to reduce manual exceptions, accelerate dispute resolution, and support clean financial posting particularly in high-volume environments.
The following response types are most commonly associated with an EDI 820:
| Response Type | Purpose | Usage Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 997 Functional Acknowledgment | Confirms receipt and basic syntax acceptance | Automatically generated in most environments |
| 999 Implementation Acknowledgment | Indicates detailed acceptance or rejection | Common in regulated, financial, and high-value ecosystems |
| 824 Application Advice | Communicates business rule or mapping exceptions | Used when remittance data requires correction |
| 812 Credit/Debit Adjustment | Communicates adjustment detail not included in the 820 | Used when a deduction requires supporting structure rather than summary billing |
What does the EDI 820 Payment Order/Remittance Advice support?
The EDI 820 supports a range of financial settlement and remittance processes, including:
- Payments covering one or many invoices
- Advance payment notifications
- Bank settlement instructions
- Deductions and promotional offsets
- Rebate or performance-based settlement
- Financial traceability and matching
- Cash application automation supporting multiple business units (ENT)
The 820 supports bundled and unbundled payment models and can function as a standalone remittance or as a system-triggered settlement instruction within an automated disbursement process.
What are the Key Features of the EDI 820 Payment Order/Remittance Advice?
| Feature Category | Description |
|---|---|
| Structured Financial Data | Captures banking detail, payment method, amount paid, and traceability attributes |
| Multi-Invoice Remittance Support | Supports payment against one or many invoices, statements, credit memos, or adjustments |
| Support for Adjustments | Communicates offsets through adjustment segments including ADX and referenced 812 transactions |
| Trace Linkage | Provides a traceable relationship between EFT movement and remittance advice via TRN |
| Global Currency Support | Supports multiple currencies without initiating a foreign exchange event |
| Multi-Entity Application | Supports allocations across multiple entities or sub-ledgers using ENT |
What is the Purpose of the EDI 820 Payment Order/Remittance Advice?
The purpose of the EDI 820 Payment Order/Remittance Advice is to establish a clear and structured communication instrument for payment and remittance alignment, replacing manual payment communication, improving reconciliation efficiency, and enabling automated financial posting.
What Information is Included in the EDI 820 Payment Order/Remittance Advice?
The information included in the EDI 820 varies based on business rules, payment type, and partner agreements, and may include references such as customer purchase order numbers, account identifiers, contract numbers, shipment identifiers, or promotional program references. The EDI 820 commonly includes:
- Payer and payee identification
- Invoice references and payment allocation details
- Bank settlement and routing information
- Total amounts paid and adjustments applied
- Date and traceability information for EFT matching
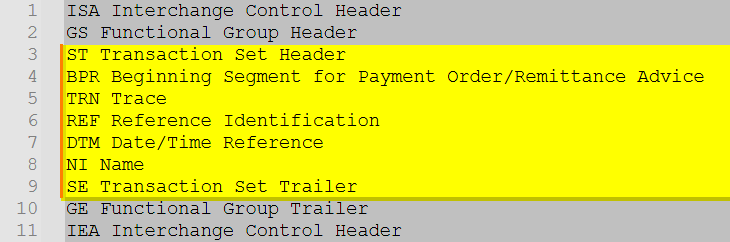
What are the Essential Components of the EDI 820?
Essential components include:
| Segment | Purpose | Selected Guidance |
|---|---|---|
| ST | Identifies the start of the transaction and control number | Control number increments per functional group requirements 820_Notes_20251208 |
| BPR | Defines payment intent, method, and settlement details | One of the most critical segments for payment execution logic 820_Notes_20251208 |
| TRN | Establishes trace identifiers linking payment to remittance | Required when remittance is separate from the bank transfer 820_Notes_20251208 |
| CUR | Specifies currency used in settlement | Does not initiate foreign exchange events 820_Notes_20251208 |
| REF | Carries reference identifiers supporting matching and reconciliation | Uses Code List 128 qualifiers 820_Notes_20251208 |
| DTM | Indicates dates relevant to settlement and posting | Supports ISO 8601 guidance 820_Notes_20251208 |
| N1/N3/N4 | Identifies payer, payee, and locations | Uses N103 qualifiers including GLN and DUNS 820_Notes_20251208 |
What Common Segments are Included in the EDI 820?
Common segments include:
| Segment | Description |
|---|---|
| ST | Transaction Set Header |
| BPR | Payment Information |
| TRN | Traceability Link |
| REF | Assigned Identifiers |
| CUR | Currency |
| N1/N3/N4 | Entity and Address Detail |
| ENT | Entity Loop Used for Multi-Organization Allocations |
| RMR | Remittance Detail Anchor |
| ADX | Adjustment Details |
| DTM | Date/Time Reference |
| SE | Transaction Trailer |
Summary Table of Key Segments
| Segment | Role in Settlement and Remittance Processing |
|---|---|
| BPR | Declares payment intent, method, and execution details |
| TRN | Ensures traceable match between remittance and financial settlement |
| RMR | Anchors invoice-level allocations and offsets |
| ADX | Communicates deduction or billing adjustments |
| ENT | Supports multi-entity remittance allocation |
What Status Codes are used with the EDI 820 Payment Order/Remittance Advice?
The EDI 820 does not rely on a single dedicated status code structure for remittance execution. Status indicators are derived from the functional purpose of the remittance and the attributes contained in the contributing segments. Status may reflect settlement type, payment condition, timing, or advisory classification depending on the originating system and business process.
Status behavior typically appears through:
- Payment method and classification as indicated in BPR
- Application detail within RMR
- Adjustment classification in ADX
- Entity allocation behavior in ENT
When used across multiple systems, the combination of BPR, TRN, RMR, and ADX provides the operational clarity needed to apply the payment accurately.
Status usage may vary by implementation; however, common indicators include:
| Status Indicator Type | Representative Source | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| Payment classification | BPR elements | Indicates how payment will be executed |
| Application status | RMR elements | Indicates whether payment satisfies invoice in full or in part |
| Adjustment classification | ADX mapping | Indicates whether a deduction or offset contributed to a difference between invoice value and settlement value |
| Traceability status | TRN | Links remittance to EFT transaction or settlement batch |
What Reason Codes are used with the EDI 820 Payment Order/Remittance Advice?
Reason codes in the EDI 820 originate from adjustment activity and are transmitted through the ADX segment. Reason codes provide clarity when the amount paid differs from the invoiced amount. Typical use cases include discounts, allowances, performance program settlements, returns, damage reconciliation, and dispute resolution.
Where the adjustment pertains directly to an invoice being settled, the reason code appears in the payment remittance. Note: Adjustments requiring dispute resolution may generate subsequent transactions or 824 Application Advice until a final settlement is reached/recorded. When an adjustment pertains to conditions unrelated to the invoice being paid, best practice dictates communication through an EDI 812 Credit/Debit Adjustment.
Reason code usage is implementation-dependent; however, common values include:
| Reason Code Category | Examples | Usage Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Promotional or pricing programs | Allowances, rebates, off-invoice incentives | Common in retail, food and beverage, CPG |
| Damage or return conditions | Defective goods, concealed damage, expiry offsets | Observed when warehouse or transit issues occur |
| Administrative or compliance-based | Data mismatch, documentation variance | Often temporary and reconciled with dispute workflow |
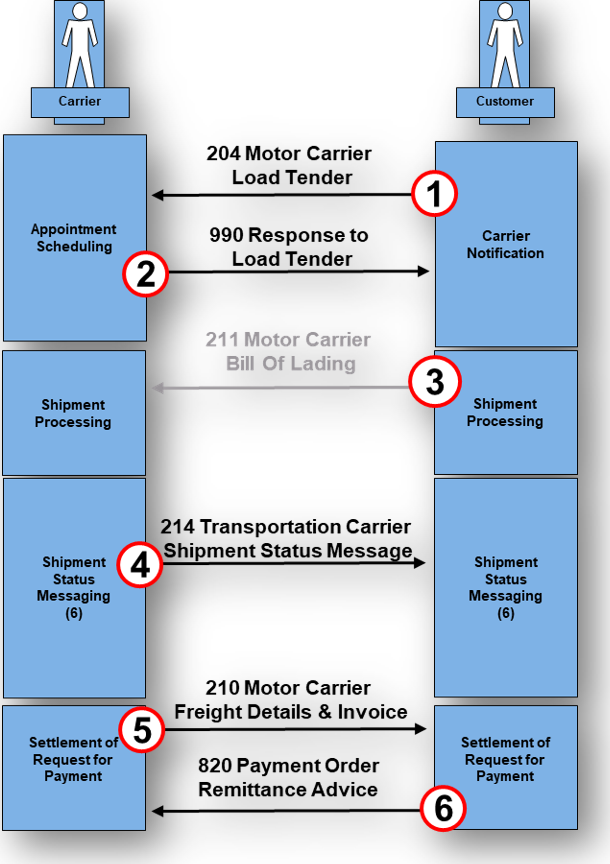
What Use Cases does the EDI 820 Payment Order/Remittance Advice support?
Use cases appear across retail, distribution, manufacturing, insurance, telecommunications, and service-based industries and include some of the scenarios below.
| Use Case Type | Description | Example Scenario |
|---|---|---|
| Settlement of multiple invoices in a single remittance | One payment may apply to a group of invoices | A distributor submits a single payment covering 274 invoices |
| Remittance prior to the financial transaction | Seller receives a pre-advice notification | A payer transmits an 820 one business day prior to funds moving |
| Separate remittance and settlement flows | Payment and remittance transmitted by separate systems | A bank executes EFT while PartnerLinQ generates advisory detail |
| Adjustment-linked settlement | Deductions included or referenced within remittance | Promotional deductions included in payment detail |
| Multi-entity allocation workflows | Remittance applies across multiple legal entities | Parent organization pays multiple subsidiaries using ENT loops |
What are the Benefits of the EDI 820 Payment Order/Remittance Advice?
| Benefit Category | Outcome |
|---|---|
| Reduced manual intervention | Eliminates manual reconciliation spreadsheets and keying efforts |
| Faster cash application | Automates matching between remittance, invoices, and banking settlement |
| Improved visibility and reporting accuracy | Enables precise ledger posting and performance analytics |
| Alignment with modern treasury workflows | Supports ACH, wire, commercial banking practices, and EFT traceability |
| Strengthened partner confidence | Provides structured transparency and audit detail |
| Reduced dispute cycle time | Enables faster resolution of deductions, offsets, or financial discrepancies |
How efficient is the EDI 820 Payment Order/Remittance Advice?
The EDI 820 provides high operational efficiency by automating remittance communication and supporting direct integration with ERP, AP/AR, treasury management, and banking platforms.
PartnerLinQ enables automated matching, additional efficiency driven through rule-driven posting and tolerance-based auto-apply logic between the 820, bank settlement, invoice history, and adjustment records in support of faster close cycles and reduced aging balances (DSO).
How compliant is the EDI 820 Payment Order/Remittance Advice? 
The EDI 820 aligns with ANSI X12 v4010 guidance and is widely accepted across domestic and international financial environments. The transaction supports ISO currency standards and financial institution routing formats while remaining consistent with GS1 and cross-industry messaging standards. PartnerLinQ supports the required security, syntax validation, envelope structure, date/time compliance, mapping and interoperability with common transmission protocols including AS2 and SFTP in support of the EDI 820.
What is the Format of the EDI 820 Payment Order/Remittance Advice?
The EDI 820 uses the ANSI X12 Payment Order/Remittance Advice transaction structure. The format supports structured segments, elements, and optional components, including conditional, required, and repeating loops. The 820 consists of a functional group within an ISA/GS envelope, a header section, and supports repeating remittance loops that include references (REFs) and adjustments (ADXs), and a transaction trailer.
How accurate is the EDI 820 Payment Order/Remittance Advice?
Accuracy depends on synchronized master data, including banking identifiers, invoice numbers, location codes, currency usage, and reason code alignment. When deployed and validated, (e.g., identifiers, automated matching rules, and control number integrity), the EDI 820 enables precise posting and automated financial reconciliation.
What are the limitations of the EDI 820 Payment Order/Remittance Advice?
Limitations generally relate to ecosystem maturity rather than the transaction itself. Accuracy depends on:
- Consistency of invoice references
- Alignment of adjustment detail
- Banking data synchronization
- Shared reason code governance
- Exception workflow automation
Where financial institutions provide locked formats or unstructured text, the 820 may serve as an advisory only rather than an automated cash application mechanism.
Are Guidelines and Sample Files for the EDI 820 Available?
Yes. PartnerLinQ provides implementation guides, testing files, and payload examples to support onboarding, mapping, validation, and cash application workflows. Documents include transaction examples, segment-by-segment notes, and support contact access.
What are the Basic Questions for EDI Integration with the EDI 820 Payment Order/Remittance Advice?
- Are there Samples and Specs available?
- What is the general direction of the transaction?
- Are they Inbound to the client or Outbound from the client to another party?
- Are there more than one trading partner exchanging the EDI 820 Payment Order/Remittance Advice?
- Are there other interested parties?
- What transactions might these interested parties be a party to?
- Will the remittance be bundled with payment or sent separately?
- Will automated matching be used, or is human review required?
- Are adjustments included, and if so, how are reason codes governed?
- What response to the transaction is expected or sent?
- Is a response to the transaction a timed event? Are notifications involved/needed?
- Are there samples and specs of the response transaction available?
- What downstream systems consume the data (ERP, finance, bank, reconciliation platform)?
- What response mechanisms are required (997, 999, 824)?
- Will cash be applied at the invoice, statement, or account level?
- How are changes to the EDI 820 Payment Order/Remittance Advice business message managed today?
- Is there automation? (an internal systems trigger) Or are EDI 820 Payment Order/Remittance Advice business message transactions triggered manually?
- Are responses and changes automatically triggered? (an internal systems trigger) Or do transactions require human intervention?
What Business-Level Workflow does the EDI 820 Support?
The EDI 820 supports workflows across:
- Accounts receivable automation
- Treasury management
- Bank integration
- Customer settlement alignment
- Deduction processing and dispute workflows
Multi-entity financial orchestration
What are the Best Practices for using the EDI 820 Payment Order/Remittance Advice?
| Best Practice | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Maintain aligned invoice and reference standards | Reduces exception processing |
| Use reason codes consistently | Supports dispute, deduction, and claims governance |
| Automate matching and exception handling | Supports faster reconciliation cycles |
| Apply multi-entity allocation where applicable | Ensures accurate ledger attribution |
| Use cross-referencing for 812-based adjustments | Clarifies discrepancies and enables dispute transparency |
What Transactions are Associated with the EDI 820 Payment Order/Remittance Advice?
| Transaction | Role |
|---|---|
| 810 | Invoice |
| 812 | Credit/Debit Adjustment |
| 824 | Application Advice |
| 997 | Functional acknowledgment |
| 999 | Implementation acknowledgment |
Footnotes
- PartnerLinQ Payment Order/Remittance Guidance.
- ANSI X12 Remittance and Settlement Processing Notes.
- PartnerLinQ v4010 Implementation Details.
- PartnerLinQ Segment Reference Notes and Mapping Rules.
About PartnerLinQ
PartnerLinQ delivers modern, cloud-based supply chain, EDI, and integration capabilities that connect trading partners, automate transactions, improve visibility, and accelerate business operations. Our platform supports global B2B connectivity, interoperability, and digital transformation with a focus on simplicity, scalability, and high-confidence execution.
For implementation support or specification requests, contact:
Contact our experts.
Explore Our Integration Solutions
PartnerLinQ Integration Solutions
Connect Everything. Integrate Intelligently.
Future-Proof Your Business with Composable, AI Powered Connectivity.



