What is the EDI 940 Warehouse Shipping Order? 
The EDI 940 Warehouse Shipping Order authorizes a warehouse or 3PL to ship inventory on behalf of a seller, replacing paper instructions with a standards-based digital command that specifies items, quantities, locations, and dates.
The Warehouse Shipping Order (940) specifies what products to ship and the quantity of each. Using this message, the seller can advise the warehouse of an original, confirmation, change, replacement, or cancellation of an order.
The seller specifies the seller’s order number, the buyer’s purchase order number, the shipping date, the buyer’s receiving location and the products to ship, their respective quantities , and other information to the warehouse operator to fulfil the shipping order.
The message supports item-based and carton-based fulfillment models and aligns with GS1 SSCC and EPC/RFID for serialized traceability.
Key functions
| Capability | Description |
|---|---|
| Authorization | Instructs warehouse to release and ship product on depositor’s behalf. |
| Execution accuracy | Communicates items, quantities, ship-to, and required ship dates. |
| Standards support | Accommodates GTIN, SSCC, EPC/RFID identifiers. |
| Fulfillment flexibility | Supports Item Warehouse Order and Carton Warehouse Order models. |
| Auditability | Establishes an electronic, traceable authorization trail. |
How does PartnerLinQ use the 940 Warehouse Shipping Order?
PartnerLinQ uses the Warehouse Shipping Order (940) to authorize the public warehouse to make a shipment to a buyer on behalf of the seller.
PartnerLinQ transforms the instruction from the ERP or OMS, validates mandatory elements in the messages before transmission, then transmits the EDI 940 transaction to the warehouse and/or 3PL partner monitoring for an EDI 945 message to reconcile progression and requested items and quantities versus shipped items and quantities. The PartnerLinQ platform supports GTIN, SSCC, EPC, and seller item codes, it also supports data elements for traceability. The EDI 940 transaction through the PartnerLinQ platform includes carrier guidance and special handling when applicable.
Execution behaviors
| Function | PartnerLinQ Role |
|---|---|
| Instruction delivery | Sends warehouse shipping orders and details to 3PLs. |
| Compliance validation | Verifies order number, ship-to, dates, quantities, codes. |
| GS1 / EPC / SSCC | Accepts serialized identifiers for pallets and cartons. |
| Lifecycle control | Reconciles release via inbound 945, updates ERP and visibility. |
What responses to the EDI 940 Warehouse Shipping Order are expected/sent? 
Warehouses respond with the EDI 945 Warehouse Shipping Advice to confirm shipment execution and variances; and the EDI 997 and EDI 999 provide syntax acknowledgments when required. The Functional Acknowledgment (997) is an ANSI X12 EDI transaction set that represents industry’s best practice and is automatically generated by modern EDI software. The Implementation Acknowledgment (999) is an ANSI X12 transaction set designed to provide detailed feedback on the acceptance or rejection of received EDI transactions. Unlike the 997, which only indicates syntactical validity, the Implementation Acknowledgment (999) also evaluates compliance against published implementation guides.
What does the EDI support?
The Warehouse Shipping Order (940) supports multi-warehouse and 3PL execution, the use of the GS1 barcode and Electronic Product Code / Radio Frequency Identification (EPC/RFID) data carriers and product serial number identification, carrier and transportation details in the W66, and special handling with the W6; and while not ideal for structured data, the NTE (Note/Special Instruction) segment is also supported.
What are the Key Features of the EDI 940 Warehouse Shipping Order?
- Digital shipping order/release authorization that eliminates paper/phone calls.
- Reduces manual errors, speeds processing, and cuts costs compared to faxes/emails.
- Structured item and carton control with W01 and SSCC/EPC.
- Extended reference details in both header and line-item segments
- Carrier and routing guidance via W66 with SCAC.
- Special handling instructions via W6, including packing slip scenarios.
What is the Purpose of the EDI 940 Warehouse Shipping Order?
The 940 directs warehouse operations to ship inventory accurately and on time while maintaining alignment with customer commitments and internal controls.
What Information is Included in the EDI 940 Warehouse Shipping Order?
Order references (seller order, buyer PO), locations (ship-to, ship-from, warehouse), item detail (SKU/GTIN, qty, UOM), logistics (carrier, method, FOB, SCAC), special handling instructions, and totals (qty, weight, volume).
What are the Essential Components of the EDI 940?
| Segment | Purpose | Selected Guidance |
|---|---|---|
| W05 | Shipping order identification | Action codes that drive downstream activity - original, cancel, replace. |
| N1 - N4 | Party and address identification | Qualifiers define depositor, ship-to, etc. |
| G62 | Date/Time | Supports ‘Must Respond By,’ Requested Ship Date/Pickup Date,’ Delivery Requested’ and other Date/Time detail. |
| W66 | Carrier information | Method/payment, FOB, SCAC. |
| W6 | Special handling information | Support for packing slips. |
| W01 | Line-item detail | Support for item, item identifiers, qty, UOM, packaging, etc. |
| N9 | Reference identification | Additional traceability reference support: serial, batch/lot, and other references. |
| W76 | Total shipping order | Qty, weight, volume; TL/LTL determination support. |
What Common Segments are Included in the EDI 940 ?
Common segments include ST, W05, N1/N3/N4, N9, G62, NTE, W66, W6, LX, W01, G69, W76, SE.
| Segment | Key Elements | Role |
|---|---|---|
| W0501 | Action code (N=Original, F=Cancel) | Controls release vs cancel/replace. |
| N103/N104 | Party qualifiers/IDs | Establishes ship-to, ship-from, warehouse identity. |
| W66 | SCAC, payment, method, FOB | Sets transportation parameters and SCAC. |
| W601 | Handling qualifier | Enables packing slip and special inserts use cases. |
| W76 | Totals | TL/LTL estimation by weight/volume. |
What Status Codes are used with the EDI 940?
Typical status and action indicators used with the EDI 940 are primarily found in the W05 Shipping Order Identification segment, specifically element W0501 (data element 473: Order Status Code). This code identifies the purpose of the transaction set, such as creating an original order, making changes, or canceling it. While there are up to twelve values for code 473, implementations for EDI 940 typically limit usage to a subset of 4–7 codes that include Original, Refresh/Update, Cancellation.
| Code | Description | Typical Use in EDI 940 |
|---|---|---|
| N | Original | Indicates a new, initial shipping order from the depositor to the warehouse. This is the most common code for standard shipments. |
| R | Change | Used to modify an existing order (e.g., update quantities, dates, or items without canceling the entire order). Requires a link to the original via W05-04 (Link Sequence Number). |
| F | Cancel | Signals full cancellation of the shipping order. Often paired with the original order number for reference. |
| G | Changes to Other than Line Items | For updates or changes to non-line-item details (e.g., carrier, dates, or totals) without altering items or quantities. |
| D | Delete | Specifies deletion of a previously transmitted order or specific line items. While not recommended, implementation is like cancellation, perhaps a bit more granular. |
| C | Confirmation | Acknowledges or confirms receipt/processing of an order (less common in 940 outbound but used in responses). |
What Reason Codes are used with the EDI 940 Warehouse Shipping Order?
The EDI 940 (Warehouse Shipping Order) transaction set does not have a dedicated set of ‘Reason Codes or a ‘Reason Code’ segment to provide rationale or explanations for cancellations, changes, rejections, or adjustments. Rationale is conveyed in some implementation using codes in the N9 Extended Reference Information segment. Related qualifiers such as "ZZ" (Mutually Defined) which allows a measure of custom code and while not ideal for structured data, the NTE (Note/Special Instruction) segment have been observed with an NTE01 Note Reference Code supplementing the ‘Reason for an Action’ with text in the NTE02 Description.
What Use Cases does the EDI 940 support?
- 3PL fulfillment for direct-to-store and direct-to-consumer models.
- Regional replenishment for retail and grocery networks.
- Export logistics with sealed pallets and serial control.
- Cold-chain execution with special handling.
| Use Case | Description | Example Scenario |
|---|---|---|
| Original Warehouse Shipping Order | Sending a new instruction to a warehouse to prepare and ship goods to one or more destinations. Includes details like items, quantities, ship-to addresses, delivery dates, and carrier info. | A retailer receives a customer order; the supplier generates an EDI 940 to instruct a remote 3PL warehouse to pick, pack, and ship products to the retail store by a specified date. |
| Multi-Destination or Multi-Item Warehouse Shipping Orders | Coordinating shipments to multiple locations or consolidating myriad items for a single destination, often with stop sequences or routing. | An e-commerce seller uses the EDI 940 to direct a fulfillment split between warehouses for efficiencies such as shipment speed/cost. |
| Special Handling Instructions | Specifying requirements like labeling, temperature control, equipment types, or substitutions for items. | A fresh or frozen food manufacturer sends an EDI 940 requiring a refrigerated trailer (W06), GS1-128 pallet labels (W601 = PBC), and LIFO shipment (condition c W0117 = 11) for perishable goods. |
| Warehouse Shipping Order Confirmation | Acknowledging or confirming a previously transmitted order, often with updated status. | While not widely used, a depositor sends a warehouse receipt confirmation EDI 940 (W501 = C) to verify processing ahead of the EDI 945 warehouse shipment advice. |
| Warehouse Shipping Order Modification or Change | Updating an existing shipping order (e.g., quantities, dates, or non-line items) *requires linking to the original via reference numbers. | A depositor wants to change the details of a shipment and sends a change EDI 940 (W0501 = R) to advise the warehouse of the change prior to receiving the EDI 945. A supplier detects an inventory error and sends a change EDI 940 (W0501 = R) to advise the depositor of reduced availability of selected items in advance of the EDI 945 warehouse shipment advice. |
| Warehouse Shipping Order Cancellations | Specifying the cancellation of a previously acknowledged Warehouse Shipping Order. | The depositor transmits an EDI 940 (W0501 = F) to stop processing, prior to receiving the EDI 945. Linked to the original order through unique identification (shipment ID), such messages typically contain only header/summary segments without details. |
What are the Benefits of the EDI 940 Warehouse Shipping Order?
- Accuracy improves because of structured item/carton detail.
- Efficiency increases because of digital release and fewer manual touches.
- Traceability strengthens with SSCC and EPC/RFID alignment.
- Audit readiness improves via standardized transaction content.
How efficient is the EDI 940? 
Warehouse Shipping Order digital automation is very efficient when compared to manual execution. The Warehouse Shipping Order process reduces the cycle times between order release and shipment confirmation and the information exchanged between parties, particularly when automatically reconciled by way of the EDI 945 with simple alerting or just exception reporting.
How compliant is the EDI 940 Warehouse Shipping Order?
The EDI 940 Warehouse Shipping Order aligns with X12 v4010 standards, GS1 SSCC, EPC guidance, and common AS2 transport practices and protocols, The 940 supports global warehouse networks and industry audit controls and is used in PartnerLinQ-connected ecosystems.
What is the format of the EDI 940 Warehouse Shipping Order?
The EDI 940 uses the ANSI X12 Warehouse Shipping Order structure for digital warehouse release and shipment initiation.
How accurate is the 940?
Accuracy depends on synchronized identifiers, location codes, and partner code lists; PartnerLinQ validations on ST/SE control numbers and mandatory content support processing integrity.
What are the limitations of the 940?
Adoption depends on partner WMS maturity, serialized handling capabilities, and agreement on refresh versus cancel/replace strategy for change management.
Are Guidelines & Sample Files for the EDI 940 Warehouse Shipping Order available?
Yes. PartnerLinQ provides sample EDI 940 Warehouse Shipping Order Transaction and implementation guides through its Support and Guideline Management Team.
Sample EDI 940 implementation guides illustrate both inbound and outbound flows, segment layouts, and valid data examples and support testing and partner onboarding. Customized specification documents for use in on boarding and technical development are available upon request.
PartnerLinQ provides:
- EDI 940 Warehouse Shipping Order transaction implementation guide
- Sample payloads
- Qualification and testing maps
- Error handling and best-practice notes

What are the Basic Questions for EDI Integration with the EDI 940 Warehouse Shipping Order?
- Are there Samples and Specs available?
- What is the general direction of the transaction?
- Are they Inbound or Outbound to another party?
- If Outbound to another party, which internal system generates the shipping instruction?
- Are there more than one trading partner exchanging the 940 Warehouse Shipping Order?
- Are there other interested parties?
- What transactions might these interested parties be a party to?
- Which parties receive the EDI 940 in a multi-partner network?
- What responses to the transaction are expected or sent?
- Is a response to the transaction a timed event?
- Which events triggers the EDI 945 and related notifications?
- Are late notifications involved/needed?
- Are there samples and specs of the response transaction available?
- Which identifiers are used: GTIN, SSCC, EPC, seller item?
- Which change method applies: refresh or cancel/replace?
- How are changes to the 940 Warehouse Shipping Order business message managed today?
- Is there automation? (an internal systems trigger) Or are 940 Warehouse Shipping Order business message transactions triggered manually today?
- Are responses and changes automatically triggered? (an internal systems trigger) Or do transactions require human intervention?
What Business Level Workflow does the EDI 940 Warehouse Shipping Order support?
The EDI 940 Warehouse Shipping Order supports workflows centered on orders including customer and consumer orders, initiation and adjustment of warehouse shipping orders, integrating with warehouse management systems (WMS), and warehouse execution. The table below highlights some key workflows.
| Workflow/Use Case | Description |
|---|---|
| Order Initiation and Dispatch Instruction | The EDI 940 delivers initial shipping directives to the warehouse, specifying picks, packs, and routes for fulfillment. |
| Inventory Allocation and Reservation | The EDI 940 can be used to reserve stock against orders, preventing overcommitment and enabling better visibility. |
| Carrier and Routing Coordination | The EDI 940 can specify transportation details to optimize logistics, including carriers, equipment, and multi-stop sequencing. |
| Exception Management and Adjustments | The EDI 940 can be used to manage mid-process changes to quantity, dates, even cancellations, maintaining order integrity. |
| Compliance and Reporting Setup | The EDI 940 can be used to embed labeling requirements and facilitate regulatory adherence (e.g., CFR Title 21, FSMA Final Rule, GS1 standards). |
What are the Best Practices for using the EDI 940 Warehouse Shipping Order?
| Best Practice | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Utilize a ‘Change-by-Refresh’ process | PartnerLinQ suggests a ‘change by refresh’ process for partners who expect Warehouse Shipping Orders to change and anticipate the use of change or replacement orders. ‘Change-by-Refresh’ ensures data consistency and reduces state drift. |
| Automate exception reporting | Accelerates issue resolution and DSO reduction. |
| Coordinate with partners | Coordinate with partners to agree on formats, schedules, and error protocols early using implementation guides to ensure compatibility. |
| Include common and essential data elements | Use SOPs to push fields population backstream. Details such as Customer PO (REF), Location (N1), Quantities/UOMs (W01), Contacts (PER), and equipment (W66) help ensure precise execution and visibility. |
| Standardize codes and normalize data | Use and validate SKUs, GTINs, SCACs, GLN, postal codes, item IDs, and their consistency; use a single source of truth. |
| Incorporate validation rules | Leverage EDI 940's built-in error-checking to flag incomplete data and enable notifications without impacting workflows. |
| Define protocols for exceptions | Use status codes (e.g., 'R' for changes) with original links; create playbooks for substitutions, backorders, or carrier updates. |
| Automate notifications and security | Set real-time alerts for failures; encrypt transmissions to protect sensitive data and maintain trust. |
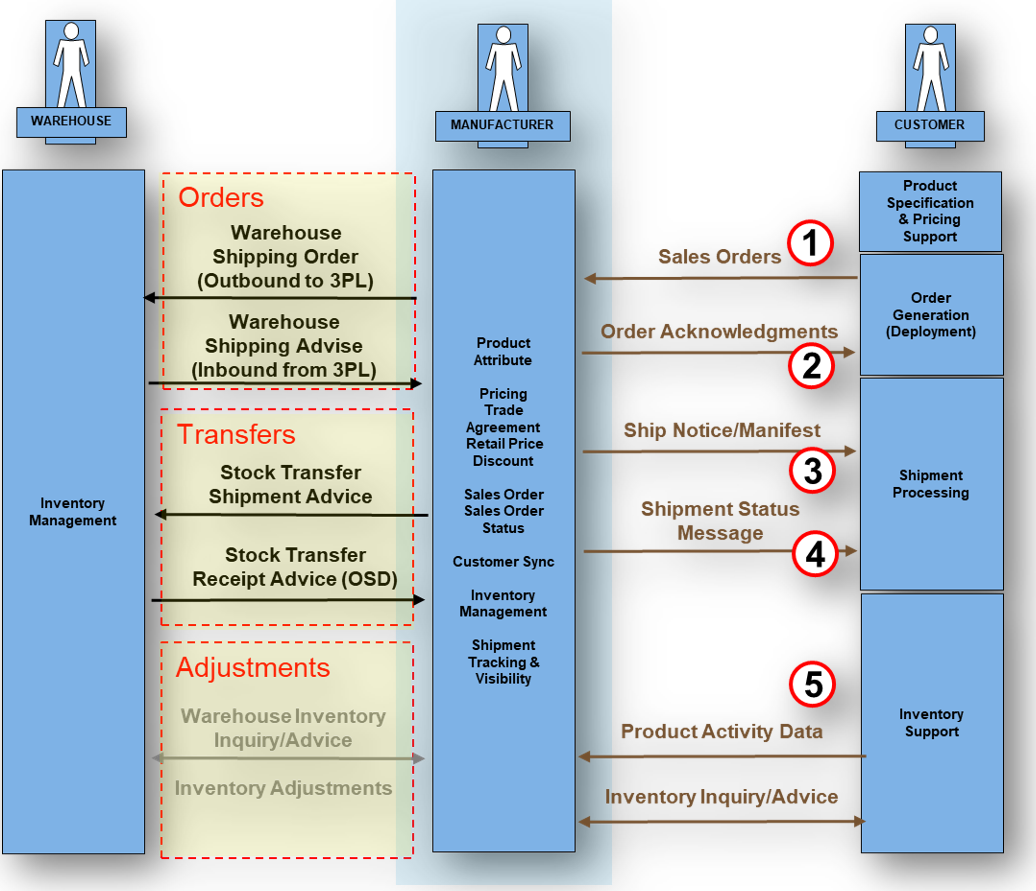
What Transactions are associated with the 940?
945 (shipment confirmation), 850 (PO), 856 (ASN), 943/944 (stock transfer), 947 (inventory adjustment), 810 (invoice), 997/999 (acks).
| Transaction | Role |
|---|---|
| 810 | Invoice following shipment confirmation |
| 850 | Purchase Order |
| 856 | Advance Ship Notice |
| 943 | Warehouse Stock Transfer Shipment Advice |
| 944 | Warehouse Stock Transfer Receipt Advice |
| 945 | Warehouse Shipping Confirmation |
| 947 | Warehouse Inventory Adjustment Advice |
| 997 | Functional Acknowledgment |
| 999 | Implementation Acknowledgment |
Footnotes
- 940 Notes and Implementation Details (SSCC/EPC, handling, identifiers).
- PartnerLinQ “How the 940 is used” notes.
- PartnerLinQ 940 v4010 PDF Guidelines (purpose, structure, segments).
- 945 Final Reference (lifecycle alignment and best practices).
- G62 “Must Respond By,” W76 totals, ST/SE control integrity details.
- G62 time conversion and qualifier use.
- W66 SCAC, payment/method, FOB, special handling via W6.
- Template headings and section structure.
- Additional N9/NTE usage and qualifier references.
- W01/G69/W76 references across examples.
Explore Our Integration Solutions
PartnerLinQ Integration Solutions
Connect Everything. Integrate Intelligently.
Future-Proof Your Business with Composable, AI Powered Connectivity.



