What is the EDI 863 Report of Test Results?
The EDI 863 Report of Test Results is the ANSI X12 transaction used to electronically transmit the results of tests performed to satisfy a specified product or process requirement between trading partners. 
The EDI 863 document eliminates manual or paper-based reporting by providing a structured, highly detailed, machine-readable form for communicating inspection results, certification findings, physical measurements, test methods, and statistical process control data.
The EDI 863 supports the reporting of quality data for component materials, finished goods, intermediate assemblies, or process outcomes. It conveys test data such as laboratory results, inspection evaluations, dimensional measurements, chemical assays, mechanical strength testing, microbiological findings, material verification results, or other compliance-driven outcomes.
How does PartnerLinQ use the EDI 863 Report of Test Results?
PartnerLinQ uses the EDI 863 in support of manufacturers, distributors, suppliers, buyers, testing laboratories, and regulated industries where product quality, consumer safety, and adherence to precise specifications are mandatory. Industries supported include:
- Automotive and steel manufacturing
- Aerospace and defense
- Food and agriculture, including FDA Food Traceability List items
- Pharmaceutical, medical device, and healthcare products
- Chemical manufacturing and processing
The EDI 863 acts as the electronic mechanism for attaching authoritative test results to a product, component, batch, lot, or serialized item as it moves through the supply chain. The transaction ensures every test result is tied to a specific unit of measure, location, laboratory, item identifier, and characteristic through structured loops, identifiers, and measurement segments.
PartnerLinQ uses the EDI 863 to electronically transmit or receive test results that validate whether a material, finished good, batch, or process meets specified requirements. The report may be generated by the testing laboratory, manufacturer, processor, or any partner responsible for performing measurements or inspections.
PartnerLinQ leverages the capabilities of the EDI 863 in the following ways:
- Identification of Products and Parties - PartnerLinQ uses the LIN loop to accurately identify the specific product, lot, serial number, batch, or heat number for which the test results apply. The N1/N3/N4 loops identify laboratories, manufacturers, ship-from facilities, or ship-to parties.
- Transmission
 of Quantitative Laboratory Data - PartnerLinQ uses MEA segments to transmit numerical values such as dimensions, weights, tolerances, variances, or statistical measurements. Multiple MEA segments may appear for a single item.
of Quantitative Laboratory Data - PartnerLinQ uses MEA segments to transmit numerical values such as dimensions, weights, tolerances, variances, or statistical measurements. Multiple MEA segments may appear for a single item. - Reporting of Test Methods - PartnerLinQ uses the TMD segment to represent the procedure used for each test, such as ASTM, ISO, USP, GS1 specifications, or proprietary methods.
- Classification and Characteristics - PartnerLinQ uses the CID segment to declare the characteristic, attribute, or class associated with a measurement, providing structured classification for multi-attribute tests.
- Document Identification and Traceability - PartnerLinQ uses BTR05 and BTR06 to support Global Document Type Identifiers (GDTI), enabling a globally unique identifier for every test report that can be encoded into a barcode or RFID tag.
- Change-by-Refresh Document Management - PartnerLinQ uses a structured approach for corrections which ensures accurate synchronization across systems and eliminates ambiguity:
- Original (BTR01 = 00)
- Cancellation (BTR01 = 01) referencing original
- Replacement Original (BTR01 = 00)
- Support for Multi-Industry Quality Requirements - PartnerLinQ uses the 863 to support food safety, industrial quality, regulatory compliance, supply chain verification, and safety audits. |
What does the EDI 863 support?
The EDI 863 supports the structured reporting of test results, inspection outcomes, certification data, and process measurement information. It supports:
- Highly Granular Test Reporting - Numerical measurements, Text-based descriptions, Pass/fail conditions, Tolerances and variances, Statistical process control values
- Multi-Attribute Testing - through repeated MEA segments and CID loops, the 863 supports multiple characteristics per item.

- Global Traceability - Product identification using UPC, GTIN, buyer item number, lot number, heat number, or serial number ensures all test results are linked to a unique item.
- Cross-Partner and Cross-System Quality Communication - The 863 facilitates laboratory-to-buyer, manufacturer-to-buyer, or supplier-to-quality-team communication of test results.
- Structured (Quality Assurance) Workflows - The 863 supports workflows where test results must be received before Shipment approval, Material acceptance, Payment authorization, Production release, and can be incorporated into production ready automations.
- Regulatory and Standards Compliance - The 863 supports industry-specific testing processes, including quality standards from Automotive and aerospace, FDA, ISO, GS1, ASTM, USP, and the Steel Industry.
What are the Key Features of the EDI 863 Report of Test Results?
The EDI 863 includes a robust set of features that enables the structured, accurate, and repeatable transmission of detailed test results between trading partners¹. These features support industries where quality control, compliance, and traceability are essential.
- Structured Test Result Reporting - The EDI 863 transaction supports structured measurement reporting through MEA segments repeated, each MEA communicating a single measurement, value, tolerance, or statistical element, making the EDI 863 highly suitable for highly regulated environments requiring precision.
- Comprehensive Item Identification - The EDI 863 transaction supports various methods of item identification in the LIN loop which identifies the specific product, component, lot, batch, heat, or serialized unit under test ensuring each test result is tied to a unique item or material instance.
- Support for Test Methods and Characteristics - The CID and TMD loops in the EDI 863 transaction allow classification of characteristics and declaration of test methodologies, enabling clear communication of the standards or procedures followed during the test.
- Support for Laboratory, Supplier, and Destination Identification - The EDI 863 transaction supports distinct party identification in the N1 loop (Max Use:* >1), The N1/N3/N4 can be used to identify the laboratory performing the test, the product owner, the manufacturer, the manufacturing plant, the receiving entity, dozens of entities (if needed) thus ensuring complete traceability.
- Support for Global Document Traceability Using GDTI - The EDI 863 transaction supports GDTI, the BTR05 and BTR06 segments can carry Global Document Type Identifier (GDTI) values, enabling globally unique test report identification across the supply chain.
- Support for Multi-Industry Requirements - The EDI 863 transaction supports automobile, aerospace, chemical, food and agriculture, steel, pharmaceutical, and medical device industries that depend on standardized quality reporting.
What is the Purpose of the EDI 863 Report of Test Results?
The purpose of the EDI 863 is to provide a formal, standardized method for communicating the results of tests conducted on a product, material, or process. The EDI 863 supports both operational and compliance-driven quality management processes and the EDI 863 document ensures both trading partners receive consistent information needed to validate whether a product meets required standards or specifications.
The EDI 863 enables trading partners to:
- Confirm conformance to product or process specifications
- Document compliance with regulatory or industry requirements
- Support operational decisions such as release, acceptance, rejection, or investigation
- Maintain traceable digital records of testing and certification
- Integrate test results directly into quality management or ERP systems
What Information is Included in the EDI 863 Report of Test Results?
The EDI 863 contains detailed, structured information across multiple layers of the testing process. The specific types of information included typically fall into the categories below.
- Identification Data – Unique identification numbers, part numbers, serial numbers, lot numbers, batch numbers, heat numbers, and identifiers for any and all parties involved in the testing process from the manufacturer to the testing lab and every facility in between.
- Certification Data - The EDI 863 Report of Test Results provides information confirming that a product, item, or process meets regulatory or customer standards.
- Inspection Data -
 The EDI 863 supports detailed inspection outcomes, including pass/fail results, visual inspection findings, testing methodologies, and compliance to specific attributes.
The EDI 863 supports detailed inspection outcomes, including pass/fail results, visual inspection findings, testing methodologies, and compliance to specific attributes. - Physical Measurement Data - The EDI 863 can also include physical attributes and metrics including dimensions, weight, density, and other physical attributes.
- Statistical Process Control (SPC) Data - Provides statistical measurements used to monitor and control manufacturing processes.
- Test Method Information - The EDI 863 supports Test Methodologies in the TMD segment documents test method identifiers, procedures, and any relevant standards.
- Dates and Traceability Data - DTM segments provide date references for test performance, test report creation, shipping, or processing which can be uniquely provided for product, component, batch, lot, or serialized item in the LIN as it moves through the supply chain.
What are the Essential Components of the EDI 863 Report of Test Results?
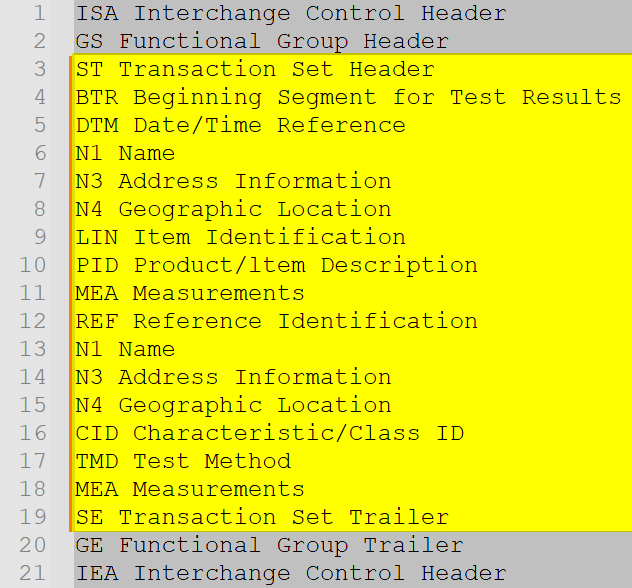
Essential Components of the EDI 863 Report of Test Results that are necessary for accurate communication of test results include the following segments aligned to the specification and used to structure the test results into easily identified, repeatable data components that can be incorporated into downstream systems automatically.
| Segment | Purpose | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| ST – Transaction Set Header | Opens and identifies the 863 transaction. | Must include transaction set code “863” and control number. |
| BTR – Beginning Segment for Test Results | Indicates purpose (original, cancellation), report type, date, and identifies the test report. | BTR01: Purpose code; BTR05–BTR06 may support GDTI. |
| DTM – Date/Time Reference | Specifies dates relevant to the test or processing activity. | Supports ISO 8601, UTC conventions, GS1 date formats. |
| N1/N3/N4 – Party Identification Loops | Identifies the testing laboratory, manufacturer, ship-from, or ship-to location. | Supports GLN, DUNS, SAN, HIN, SCAC. |
| LIN – Item Identification | Identifies the item being tested. | Links MEA measurements to the correct product. |
| PID – Item Description | Provides descriptions of the item. | Supports coded or free-form descriptions. |
| MEA – Measurements | Reports the actual test results. | Supports multiple measurements, tolerances, and SPC data. |
| REF – Reference Identification | Communicates lot, batch, serial, or other reference identifiers. | Supports cross-reference of external documents. |
| CID – Characteristic/Class ID | Specifies the characteristic or class being measured. | Provides classification for the test attribute. |
| TMD – Test Method | Declares the test procedure used. | Supports ASTM, ISO, USP, GS1, and proprietary methods. |
| SE – Transaction Set Trailer | Terminates the transaction and confirms segment count. | Ensures document integrity. |
What are the Common Segments Included in the EDI 863 Report of Test Results?
The following segments appear in most or all EDI 863 implementations and define the core transactional structure.
| Segment | Name | Function |
|---|---|---|
| ST | Transaction Set Header | Identifies the start of the 863 and assigns unique control number. |
| BTR | Beginning Segment for Test Results | Defines purpose, date, and identifiers for the test report. |
| DTM | Date/Time Reference | Supplies relevant dates, including testing or processing. |
| N1 / N3 / N4 | Party Identification | Identifies laboratories, facilities, senders, and receivers. |
| LIN | Item Identification | Identifies the product, component, lot, or batch under test. |
| PID | Item Description | Provides item description or characteristics. |
| MEA | Measurements | Communicates measurement values or test results. |
| REF | Reference Identification | Provides supplementary identifiers (lot, batch, serial). |
| CID | Characteristic/Class ID | Declares a characteristic being tested. |
| TMD | Test Method | Communicates the specific test method used. |
| SE | Transaction Set Trailer | Completes the transaction and verifies segment count. |
What Status Codes are used with the EDI 863 Report of Test Results?
The EDI 863 Report of Test Results does not include a dedicated “Status Code” segment (unlike the 824 or 855). However, the EDI 863 transaction does conveys operational status through the BTR01 – Transaction Set Purpose Code, which functions as the document’s status indicator.
| Status Code | Meaning | Usage Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 00 | Original | Used when communicating new test results for the first time. |
| 01 | Cancellation | Used to cancel a previously submitted 863; must reference the original report ID in BTR05. |
| 28 | Query | Technically supported but not recommended for production use; the 28 qualifier is somewhat limited to exploratory use or work-group scenarios for testing. A production use has yet to be confirmed. |
PartnerLinQ considers 00 and 01 the primary operational status codes that drive the test result lifecycle. Corrections or updates follow a change-by-refresh methodology which instructs the sender to send a cancellation (01), then send a replacement EDI 863 (00).
What Reason Codes are used with the EDI 863 Report of Test Results?
The EDI 863 does not contain a dedicated “Reason Code” segment for defining acceptance or rejection reasons. However, the REF segment may carry qualifiers from X12 Code List 128 to identify documented reasons or identifiers.
PartnerLinQ uses the REF segment when reference data must be exchanged and cannot be derived locally by the receiving partner. These codes are not “reasons” in the classic sense, they are however used within the EDI 863 to convey additional reference information related to:
- Test documentation
- Lab certifications
- Batch or lot identifiers
- Customer or supplier reference numbers
- Process or material identification
Reason-like context (e.g., why a test was run or the type of test) can be communicated through the BTR04 Report Type Code (e.g., IU Inspection Result, LA Laboratory Results, MR Material Inspection and Receiving Report, QR Quality Report), CID02 segment Product/Process Characteristic Code (e.g., 68 Chemistry, 71 Mechanical), and TMD02 Agency Qualifier Code segment (e.g., ST American Iron & Steel Institute, AP American Petroleum Institute, AT American Society for testing and Material (ASTM)) considering traditional Reason Codes don’t exist through X12 V8020.
What Use Cases does the EDI 863 Report of Test Results support?
The EDI 863 supports a variety of industries and operational environments that require structured reporting of test results³. The following use cases represent the most common use cases for the EDI 863 Report of Test Results.
- Quality Assurance
Used when buyers require test results prior to shipment release, material acceptance, or payment authorization. - Regulatory Compliance
Used by industries such as food processing, agricultural production, pharmaceuticals, medical devices, and chemicals to report test data required by regulatory bodies or industry standards.
- Material Inspection
Manufacturers use the 863 to validate that raw materials or components meet requirements before they enter production. - Process Control and Statistical Evaluation
The MEA segments support SPC measurements to confirm that production processes remain within control limits. - Certificate and Specification Reporting
Testing laboratories use the 863 to provide laboratory results, certification data, and reports tied to a specific lot, batch, or serial number. - Multi-Partner Supply Chain Testing
Supports scenarios where results must flow from the testing lab → supplier → manufacturer → buyer.
What are the Benefits of the EDI 863 Report of Test Results?
The EDI 863 provides significant operational and compliance-related benefits⁴ in addition to its ability to support a variety of industries, operations and environments that require a form of structure when reporting of test results.
- Enhanced Quality Control
Test results delivered electronically, enable receiving systems to make automated (pass/fail) decisions about products, raw materials, component products and vendors, taking quality control to new levels of evaluation and control of supply chains. - Faster Processing and Material Release
Digitized test data increases supply chain velocity , reducing production delays caused by manual audits and review processes
- Global Traceability
The EDI 863 supports Global Traceability efforts and includes traceability capacity for GLN, DUNS, SAN, HIN, GDTI, lot numbers, serial numbers, EPC, RFID, hundreds of unique identifiers enabling end-to-end traceability within verticals and across global supply chains. - Improved Accuracy of Test Reporting
The structured segments of the EDI 863 Report of Test Results reduce reliance on manual transcription and serve to eliminate inconsistencies in reporting and formats. - Improved Trade Partner Onboarding
Standardized reporting accelerates onboarding and maintenance cycles for new suppliers even laboratories particularly when it comes to KPIs like supplier assessment, performance, ratings, and score carding. - Reduced Costs
Electronic reporting supported by the EDI 863 Report of Test Results removes paper handling, manual validation, and the burdensome administrative of managing physical documentation, facilitating wholly automated solutions for traceability. - Support for Digital Transformation
The EDI 863 integrates easily with Quality Management System (QMS),, Laboratory Information Management System (LIMS), Material Requirements Planning (MRP) systems, ERP, even WMS, and manufacturing systems, supporting automation throughout the enterprise and across various industry-specific testing methods.
How efficient is the EDI 863 Report of Test Results?
The EDI 863 Report of Test Results is a very efficient transaction document. Flexible, the EDI 863 increases efficiency by enabling automated data flows for quality results that would otherwise require manual interpretation or time-consuming review.
Efficiencies and improvements of the EDI 863 Report of Test Results include:
- Faster communication of critical testing information
- Automated ingestion into ERP and quality systems
- Less manual touch time and fewer transcription errors
- Improved cycle time for procurement, production, and distribution
- Enhanced exception management and quality routing
The EDI 863 transaction supports structured measurements, multi-level loops and is extremely scalable even for materials requiring extensive testing or chemical analysis, like those that exist in Steel and Food production, even healthcare.
How Compliant is the EDI 863 Report of Test Results?
The EDI 863 Report of Test Results is built for and ensures compliance through normalization and required segments, by identifying missing or incomplete data, and by validating data structures before transmission and on receipt, here are a few examples:
- ANSI X12 standards for structure, syntax, and code lists
- ASTM, ISO, USP, and industry-specific testing methods
- FDA Food Traceability List requirements
- GS1 GTIN, GLN, EPCIS and GDTI standards
- ISO 8601 date/time standards
- Quality assurance best practices
What is the Format of the EDI 863 Report of Test Results?
The EDI 863 follows the ANSI X12 syntax…
- Segment terminators: hex 15 (NAK) or hex 7E (~)
- Element separators: hex 7C (|) or hex 2A (*)
- Sub-element separators: **hex 3E (>) **⁶
The EDI 863 also uses a hierarchical structure which provides consistent formatting for automated translation and ingestion.
- Header area (ST, BTR, DTM)
- Name/Location loops (N1/N3/N4)
- Detail loops (LIN, PID, MEA, REF, CID, TMD)
- Summary area (SE)
How Accurate is the EDI 863 Report of Test Results?
The accuracy of the 863 is driven by way of data structure and data carrier capabilities. Structured validation ensures that only complete test results are transmitted and received and accuracy is further improved by use of globally unique identifiers (LIN, GTIN, GLN, GDTI) and standardized reference values (MEA, REF, Code List 128, TMD)
- Precise product identification via LIN
- Location/Facility identification via N1
- Reference Values via REF
- Exact measurement reporting through MEA
- Classification using CID
- Test method documentation via TMD
What are the Limitations of the EDI 863 Report of Test Results?
While the EDI 863 is highly flexible, it does have limitations Despite these limitations, the 863 remains highly adaptable across industries, limitations observed include:
- The EDI 863 does not include a dedicated acceptance/rejection segment

- Reason Codes are not native to the EDI 863 Report of Test Results and must be conveyed through descriptive segments such as the BTR, REF, CID, and TMD.
- Measurement loops must be carefully managed to avoid exceeding partner-defined thresholds.
- Complex testing scenarios may require TMD and CID loops to be fully modeled to ensure clarity.
Are Guidelines & Sample Files for the EDI 863 Report of Test Results?
Yes. PartnerLinQ provides customized EDI Specification Documents for the 863 transaction at no cost to trading partners⁷. These documents include:
- Technical guidelines
- Segment-level mapping
- Code list usage
- Sample EDI files
- Testing instructions
- Contact information for guideline support
Trading partners may request additional sample files or clarifications by contacting our experts.
What are the Basic Questions for EDI Integration with the EDI 863 Report of Test Results?
Trading partners considering or integrating the EDI 863 should consider questions like these to determine segment usage, loops required, and data quality rules; discussing them with trading and lab partners to facilitate the transition to an electronic mechanism for attaching authoritative test results to a product, component, batch, lot, or serialized item as it moves through the supply chain
- Are there Samples and Specs available?
- What is the general direction of the transaction?
- Are they Inbound to the client or Outbound from the client to another party?
- Are there more than one trading partner exchanging the 947 Warehouse Inventory Adjustment Advice?
- Are there other interested parties?
- What transactions might these interested parties be a party to?
- What response to the transaction is expected or sent?
- Is a response to the transaction a timed event? Are notifications involved/needed?
- Are there samples and specs of the response transaction available?
- How are changes to Test Results managed today?
- Is there automation? (an internal systems trigger) Or are the EDI 863 Report of Test Results business message transactions triggered manually?
- Are responses and changes automatically triggered? (an internal systems trigger) Or do transactions require human intervention? Which items or materials require test results?
- Which laboratories or facilities generate the test reports?
- Which identifiers will be used (GLN, GTIN, GDTI, lot numbers, serial numbers)?
- Which test methods must be communicated?
- Which measurements are required?
- Are the results needed before shipment, after receipt, or during production?
- Will GDTI be used for global document traceability?
- What are the required date and time formats?
- Does the receiving system support multiple MEA loops?
- Are cancellation and replacement reports expected?
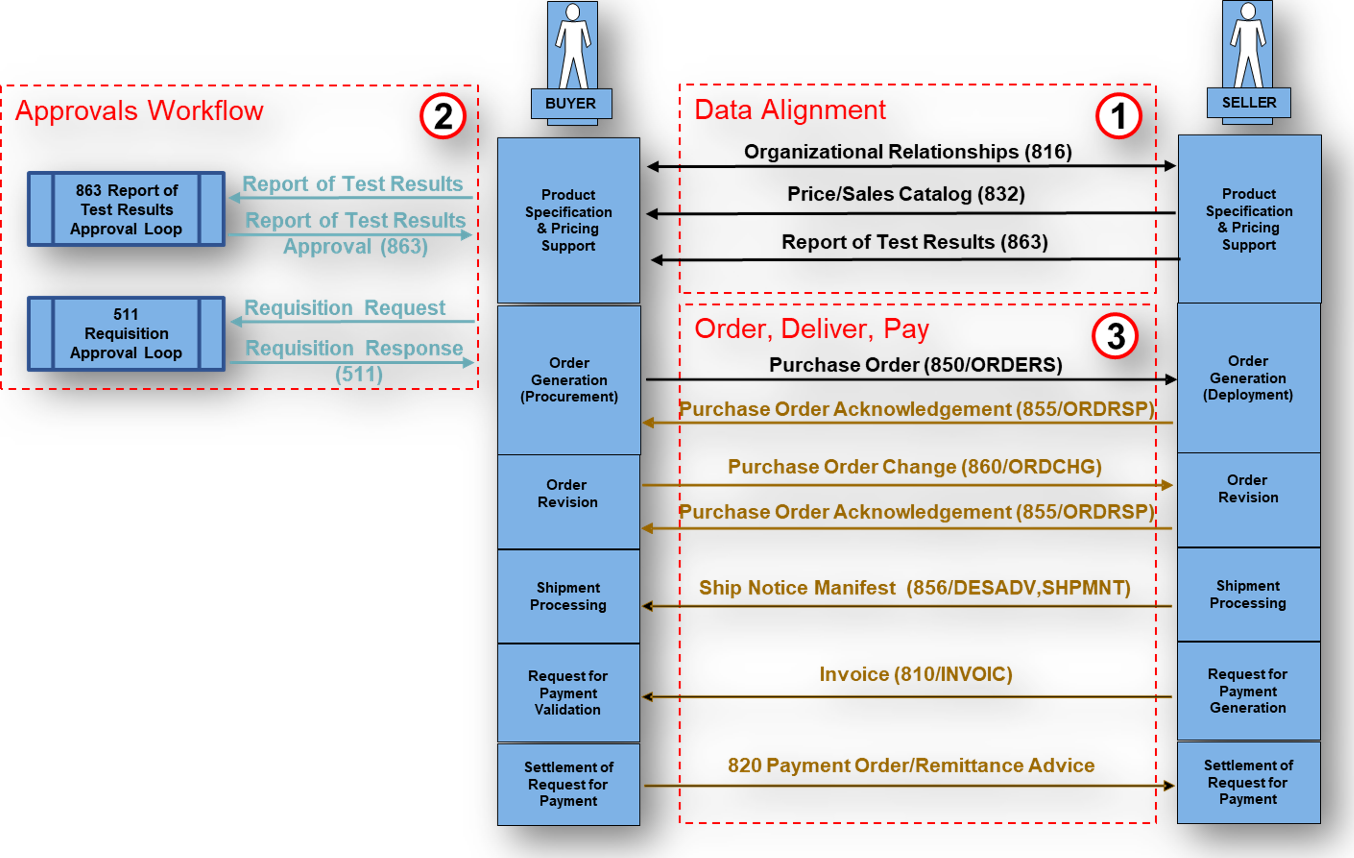
What Business Level Workflow does the EDI 863 Report of Test Results support?
A typical EDI 863 Report of Test Results document fits naturally into a quality assurance, supplier onboarding, regulatory reporting, and material verification workflow. The EDI 863 workflow typically begins with a buyer placing a requisition or an order for goods that require specific tests or quality checks (often initiated by an EDI 850 Purchase Order or similar document) before inclusion of those goods into a finished product for example, the testing process unfolds from that initial requisition or order for goods and includes: 
- Buyer places a requisition or an order for goods that require specific tests or QA
- Manufacturer or testing lab performs requested or standardized tests.
- Lab produces test results
- Lab generates the EDI 863 Report of Test Results.
- The EDI 863 is transmitted to the buyer.
- Buyer processes the results.
- Buyer issues a 997 Functional Acknowledgment.
- Systemic automation updates the quality records and/or authorizes next steps (release, payment, production).
What are the Best Practices for using the EDI 863 Report of Test Results?
These best practices strengthen traceability, quality assurance, and automated processing.
- Use a unique location identifier such as a GLN or DUNS for all locations.
- Ensure laboratories and other parties are clearly identified using N1/N3/N4.
- Use Global Document Type Identifier (GDTI) for unique test report identification.
- Follow a change-by-refresh process for corrections.
- Include item-level details in LIN/PID to avoid ambiguity.
- Maintain accurate lot/batch/serial reference values in LIN/REF
- Provide test method details using TMD loops.
- Structure measurements using repeated MEA segments.
- Provide complete date/time information using DTM with ISO 8601 conventions.
What Transactions are associated with the EDI 863 Report of Test Results?
Associated transactions work together with the EDI 863 Report of Test Results to support procurement, quality, and supply chain operations.
- 850 – Purchase Order (initial order may require tests)
- 860 – Purchase Order Change
- 869 – Order Status Inquiry (may request the status of testing)
- 840 – Request for Quotation (testing may be part of RFQ requirements)
- 814 – General Request (may serve as a testing request mechanism)
- 997 – Functional Acknowledgment (primary response to the 863)
Footnotes
- BTR01 Purpose Codes, PartnerLinQ 863 Spec
PartnerLinQ 863 v4010 20251124 - REF Code List 128, PartnerLinQ Notes
863_Notes_20251124 - Key Data Types, PartnerLinQ Notes
863_Notes_20251124 - Essential Components, PartnerLinQ Spec
PartnerLinQ 863 v4010 20251124 - Efficiency discussion, PartnerLinQ Quality Use Cases
863_Notes_20251124 - Production delimiters, PartnerLinQ Notes
863_Notes_20251124 - Guidelines availability, PartnerLinQ Notes
863_Notes_20251124 - Workflow steps, PartnerLinQ Specification
PartnerLinQ 863 v4010 20251124
Explore Our Integration Solutions
PartnerLinQ Integration Solutions
Connect Everything. Integrate Intelligently.
Future-Proof Your Business with Composable, AI Powered Connectivity.



