What is the EDIFACT INVOIC?
The EDIFACT INVOIC message is the EDI standard for electronic invoicing internationally. It enables buyers to request payment for goods or services from suppliers in a structured, automated format.
EDIFACT INVOIC message is the EDI standard for electronic invoicing internationally. It enables buyers to request payment for goods or services from suppliers in a structured, automated format.
Where the EDI 810 Invoice transaction is detail-rich, used mostly in North America and perhaps a bit rigid depending on trade relationships, the EDIFACT INVOIC message is a document tailored for Europe and international trade, United Nations (UN) based and a bit more flexible on structure.
The EDIFACT INVOIC message replaces paper-based invoices with structured, machine-readable data that allows seamless automated billing, payment processing, and reconciliation. Implementing the INVOIC message, ensures accuracy, security, and compliance across global supply chains.
Similar in purpose to the X12 810 Invoice, both are electronic invoices sent by sellers to buyers to communicate billing information for goods and services between trading partners and include details like Order numbers, prices, quantities, and taxes to request payment. Selling organizations can transmit a complete EDIFACT INVOIC Invoice transaction, a machine‑readable invoice that drives automated posting, cash application, and reconciliation with their trading partner counterparts.
in purpose to the X12 810 Invoice, both are electronic invoices sent by sellers to buyers to communicate billing information for goods and services between trading partners and include details like Order numbers, prices, quantities, and taxes to request payment. Selling organizations can transmit a complete EDIFACT INVOIC Invoice transaction, a machine‑readable invoice that drives automated posting, cash application, and reconciliation with their trading partner counterparts.
How does PartnerLinQ use the EDIFACT INVOIC?
The EDIFACT INVOIC message is generated by suppliers after shipment confirmation and aligns the message to purchase Order and receipt records for three‑way matching. The result is a electronic bill to buyers for goods and services provided. PartnerLinQ leverages the EDIFACT INVOIC transaction to automate the procure-to-pay lifecycle. The INVOIC message ties directly to corresponding purchase order and despatch advice. This enables precise three-way matching, allowing finance systems to post validated invoices automatically while maintaining full audit traceability.
What responses to the EDIFACT INVOIC are expected/sent?
PartnerLinQ trading partners typically exchange the following related documents to complete the end-to-end invoice and order management process.
| Transaction | Role |
|---|---|
| CONTRL | Functional Acknowledgment |
| DESADV | Despatch Advice |
| ORDERS | Purchase Order |
| ORDRSP | Order Response |
| ORDCHG | Order Change Request |
How do we support the EDIFACT INVOIC?
PartnerLinQ  provides complete technical enablement for INVOIC, including prebuilt maps, validations, and error management tools. The platform supports AS2, SFTP, and VAN connectivity and offers dashboard-based monitoring for message flow, acknowledgments, and business exceptions.
provides complete technical enablement for INVOIC, including prebuilt maps, validations, and error management tools. The platform supports AS2, SFTP, and VAN connectivity and offers dashboard-based monitoring for message flow, acknowledgments, and business exceptions.
What are the Key Features of the EDIFACT INVOIC?
• Automates billing workflows across international markets
• Supports multiple currencies and tax configurations
• Enables three-way matching for order, shipment, and invoice
• Reduces manual reconciliation and accelerates payment processing
• Complies with UN/EDIFACT D96A syntax and ISO 9735 standards
What is the Purpose of the EDIFACT INVOIC?
The  purpose of the INVOIC message is to electronically communicate invoice information for single or recurring billing by the seller to the buyer (typically). It ensures that billing data corresponds to delivered goods or services, enabling automated posting and faster settlement cycles.
purpose of the INVOIC message is to electronically communicate invoice information for single or recurring billing by the seller to the buyer (typically). It ensures that billing data corresponds to delivered goods or services, enabling automated posting and faster settlement cycles.
What Information is Included in the EDIFACT INVOIC?
The INVOIC message typically contains:
- Product details, quantities, and unit prices
- Invoice number and date
- Seller and buyer identifiers
- Related purchase order and shipment references
- Discounts, allowances, and charges
- Taxes, totals, and terms
What are the Essential Components of the EDIFACT INVOIC?
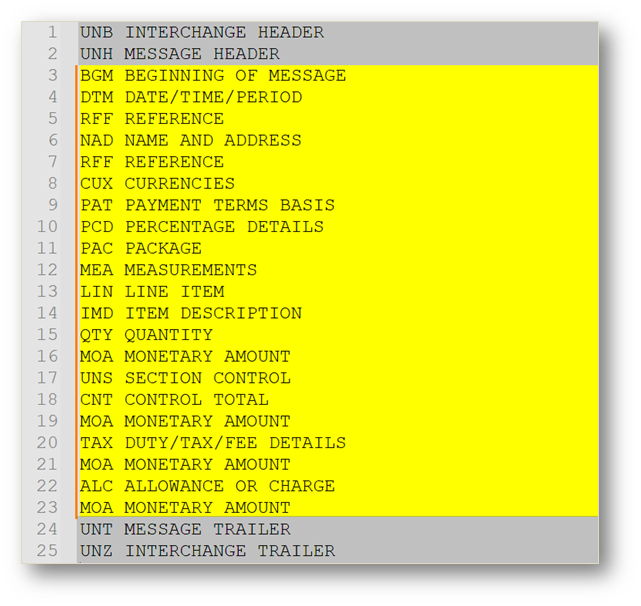
Core segments include:
| Segment | Name | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| UNH | Message Header | Indicates the start of a transaction set. |
| BGM | Beginning of Message | Uniquely identifies the invoice. |
| DTM | Date/Time/Period | Used to indicate or specify pertinent processing and other dates and times relative to the transaction. |
| RFF | Reference Information | Carries reference details between the trading parties. |
| NAD | Name and Address | Used to identify trade parties. |
| CUX | Currencies | Defines the currency expected for payment. |
| LIN | Line Item | Used to specify details about individual items or products being ordered. |
| IMD | Item Description | Used to describe the product or service being invoiced. |
| MOA | Monetary Amount | Used to convey financial values such as line totals or grand totals. |
| TAX | Tax Information | Specifies the tax type. |
| UNT | Message Trailer | A service segment that signals the end of a message. |
What are the Common Segments Included in the EDIFACT INVOIC?
Typical messages include: UNH, BGM, DTM, RFF, NAD, CUX, LIN, IMD, MOA, TAX, UNT.
Optional segments include ALC (Allowances/Charges), FTX (Free Text), and TDT (Transport Details).
| Segment | Name | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| UNH | Message Header | Identifies the start and control number. |
| BGM | Beginning of Message | Defines document type and number. |
| DTM | Date/Time/Period | Specifies critical transaction dates. |
| RFF | Reference | Links related orders and shipments. |
| NAD | Name and Address | Identifies buyer, seller, and remittance parties. |
| LIN | Line Item | Defines item number, quantity, and price. |
| MOA | Monetary Amount | Summarizes totals and subtotals. |
| TAX | Tax Information | Provides tax type and rate details. |
| UNT | Message Trailer | Closes message and validates segment count. |
What Status Codes are used with the EDIFACT INVOIC?
BGM1225  defines document status such as 9 = Original, 7 = Duplicate, and 5 = Replace. PartnerLinQ ensures consistency across message lifecycles and correlates CONTRL acknowledgments accordingly.
defines document status such as 9 = Original, 7 = Duplicate, and 5 = Replace. PartnerLinQ ensures consistency across message lifecycles and correlates CONTRL acknowledgments accordingly.
What Reason Codes are used with the EDIFACT INVOIC?
Common reasons for variance, where BGM1225 = 5 (Replace) include pricing discrepancies, tax errors, and quantity mismatches. PartnerLinQ manages financial adjustments through structured ALC and MOA segments for traceable reconciliation.
What Use Cases does the EDIFACT INVOIC support?
- Supplier billing for goods and services
- Freight invoicing for logistics providers
- Service contracts and project-based billing
- Consolidated invoices for multi-location deliveries
What are the Benefits of the EDIFACT INVOIC?
- Accelerates cash flow
- Improves accuracy and reduces disputes
- Ensures tax and compliance accuracy
- Enables global interoperability
How efficient is the EDIFACT INVOIC?
Very,  and PartnerLinQ transaction document routing validates invoices automatically, isolating exceptions for rapid correction.
and PartnerLinQ transaction document routing validates invoices automatically, isolating exceptions for rapid correction.
How Compliant is the EDIFACT INVOIC?
The EDIFACT INVOIC conforms to UN/EDIFACT and GS1 standards ensuring alignment with international B2B practices.
What is the Format of the EDIFACT INVOIC?
The EDIFACT INVOIC uses hierarchical segments grouped into Header, Detail, and Summary levels following ISO 9735 formatting rules.
How Accurate is the EDIFACT INVOIC?
PartnerLinQ enforces validation between order, shipment, and invoice data for complete accuracy.
What are the Limitations of the EDIFACT INVOIC?
The primary limitation of the EDIFACT INVOIC is the Free-Text (FTX) segments, which can reduce automation. Partners should use structured data wherever possible, and avoid Free-Text (FTX) segments.
Are Guidelines & Sample Files for the EDIFACT INVOIC transaction?
Yes. PartnerLinQ provides sample EDIFACT INVOIC Transaction and implementation guides are available through its Support and Guideline Management Team.
Sample EDIFACT INVOIC implementation guides illustrate both inbound and outbound flows, segment layouts, and valid data examples and support testing and partner onboarding. Customized specification documents for use in on boarding and technical development are available upon request.
PartnerLinQ provides:
- EDIFACT INVOIC transaction implementation guide
- Sample payloads
- Qualification and testing maps
- Error handling and best-practice notes
What are the Basic Questions for EDI Integration with the EDIFACT INVOIC?
When integrating the EDIFACT INVOIC transaction, key questions include:
- Is the transaction inbound or outbound relative to the ERP?
- Are there Samples and Specs available?
- What is the general direction of the transaction?
- Are there other interested parties?
- What transactions might these interested parties be a party to?
- What response(s) to the transaction are expected or sent
- What payment terms and currency details are required?
- Are Service, Allowance, or Charge (SAC) segments expected?
- What about taxes? (TXI)
- What system triggers the 810 – manual or automated?
- Is there automation? (an internal systems trigger) or are Invoice (810) business message transactions triggered manually?
- How are invoice updates or changes handled?
- Are responses and changes automatically triggered? (an internal systems trigger) or do transactions require human intervention?
- What about terms of payment that come from inbound orders, how will those be accommodated/validated?
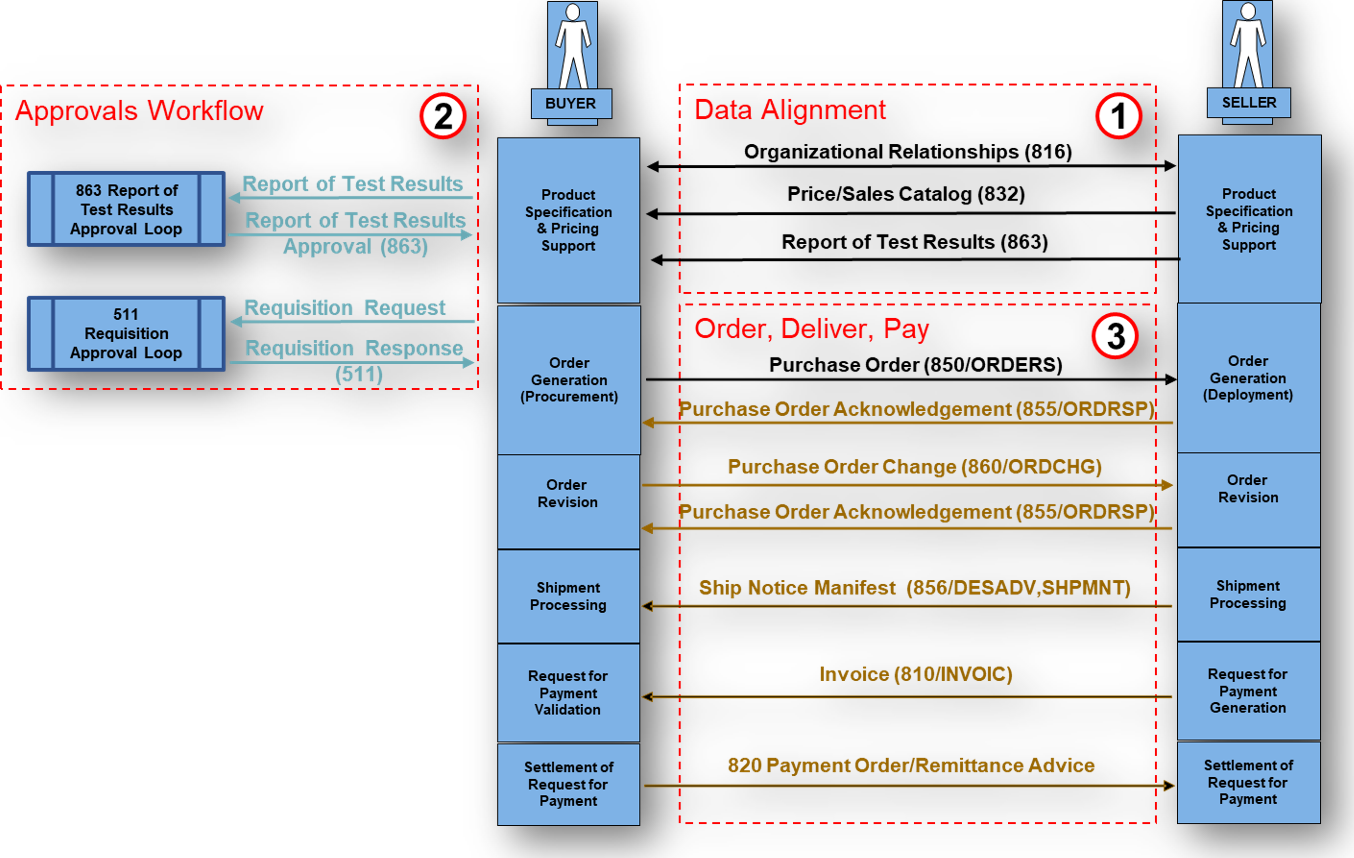
What Business Level Workflow does the EDIFACT INVOIC support?
- Seller ships goods and issues DESADV.
- Seller transmits INVOIC to buyer.
- Buyer validates and returns CONTRL acknowledgment.
- Payment initiated through PAYMUL or PAYORD.
What are the Best Practices for using the EDIFACT INVOIC?
- Maintain sequential UNH/UNT references
- Use structured RFF references
- Validate CUX and TAX accuracy
- Avoid redundant free-text entries
- Monitor message status using PartnerLinQ dashboards
What Transactions are associated with the EDIFACT INVOIC?
| Transaction | Role |
|---|---|
| ORDERS | Purchase Order |
| ORDRSP | Order Response |
| DESADV | Despatch Advice |
| CONTRL | Functional Acknowledgment |
| APERAK | Application Acknowledgment |
| PAYMUL/PAYORD | Payment Messages |
Footnotes
- UN/EDIFACT
 D96A Standard, INVOIC Message Structure – United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE).",
D96A Standard, INVOIC Message Structure – United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE).", - PartnerLinQ EDIFACT INVOIC Notes (20251009) – User Notes 3: What is the EDIFACT INVOIC message.",
- PartnerLinQ INVOIC EDIFACT vD96A (20240926) – Segment Definitions for UNH, BGM, DTM, RFF, NAD, CUX, LIN, IMD, MOA, TAX, UNT.",
- PartnerLinQ Implementation Guidance – Procure-to-Pay Automation and Three-Way Match Framework
- PartnerLinQ Connectivity & Compliance Suite – AS2, SFTP, and VAN Integration Guidelines
- UN/EDIFACT ISO 9735 Syntax Rules – Delimiter and Segment Structure Definitions.",
- PartnerLinQ Global EDI Practice – Validation, Acknowledgment, and Exception Management Framework.",
- PartnerLinQ Mapping Guidelines – D96A-to-ERP Field Alignment and Business Rule Enforcement.",
- PartnerLinQ Testing & Certification Process – INVOIC Implementation Compliance Procedures.",
- GS1 Global Standards – Application Identifiers and GLN Usage in EDI Transactions."
Explore Our Integration Solutions
PartnerLinQ Integration Solutions
Connect Everything. Integrate Intelligently.
Future-Proof Your Business with Composable, AI Powered Connectivity.



