What Is EDI?
 Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) is the structured, computer-to-computer exchange of business documents between organizations using standardized formats. Unlike paper or email-based methods, EDI automates the transfer of purchase orders, invoices, shipping notices, and other key documents. This approach eliminates back-office inefficiencies and brings clarity to transactions once trapped inside a 'black box.'
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) is the structured, computer-to-computer exchange of business documents between organizations using standardized formats. Unlike paper or email-based methods, EDI automates the transfer of purchase orders, invoices, shipping notices, and other key documents. This approach eliminates back-office inefficiencies and brings clarity to transactions once trapped inside a 'black box.'
Why does EDI matter?
EDI matters because it transforms routine operations into strategic enablers of growth. Companies using EDI can reduce transaction times by as much as sixty percent, while simultaneously reducing the frequency of costly manual errors. Rather than remaining buried as a hidden back-office utility, EDI dramatically improves efficiency, accuracy, and compliance by providing transparency and ensuring that all stakeholders operate with the same real-time information. Lastly, EDI empowers businesses with visibility across their supply chains by eliminating black-box communication and creating a foundation for sustainable, scalable growth.
Is there a brief History of EDI?
The  origins of EDI date back to just before the Industrial Revolution the dawn of technology with the development of the telegraph and onset of the American Civil War. Advancing some 50 years later with the growth of trans-oceanic trade, EDIs more familiar, modern origins begin nearly 100 years later during the 1960s, when defense and transportation organizations sought standardized ways to exchange information. During the 1970’s and 80s, industries such as retail and automotive adopted EDI to manage their supply chains. Companies like Ford, Kroger, Walmart and others leading the way in parallel with supportive technologies including FTP, HTTP and the Universal Product Code (UPC). Over time, standards such as ANSI X12 and EDIFACT emerged to ensure global interoperability, integrating with increasingly modern platforms.
origins of EDI date back to just before the Industrial Revolution the dawn of technology with the development of the telegraph and onset of the American Civil War. Advancing some 50 years later with the growth of trans-oceanic trade, EDIs more familiar, modern origins begin nearly 100 years later during the 1960s, when defense and transportation organizations sought standardized ways to exchange information. During the 1970’s and 80s, industries such as retail and automotive adopted EDI to manage their supply chains. Companies like Ford, Kroger, Walmart and others leading the way in parallel with supportive technologies including FTP, HTTP and the Universal Product Code (UPC). Over time, standards such as ANSI X12 and EDIFACT emerged to ensure global interoperability, integrating with increasingly modern platforms.
Is EDI relevant?
EDI  has remained relevant, despite APIs, XML, and cloud systems evolving from a back-office utility to a front-line highly competitive strategic investment. Driven largely by large retailers and automotive manufacturing giants who mandated adoption among suppliers, EDI was further developed through standards committee responsible for developing, maintaining, and interpreting X12 standards. The use of subcommittees effectively streamlining supply chains (X12M) 9 and transactions in support of supply chains including communications and control transactions (X12C) 7, Transportation (X12I) 8, and even insurance (X12N) 10. Today, EDI continues to evolve, integrating with APIs, cloud platforms, and advanced analytics, an evolution that reflects its transition from a hidden black box, back-office process into a visible driver of competitive business practices.
has remained relevant, despite APIs, XML, and cloud systems evolving from a back-office utility to a front-line highly competitive strategic investment. Driven largely by large retailers and automotive manufacturing giants who mandated adoption among suppliers, EDI was further developed through standards committee responsible for developing, maintaining, and interpreting X12 standards. The use of subcommittees effectively streamlining supply chains (X12M) 9 and transactions in support of supply chains including communications and control transactions (X12C) 7, Transportation (X12I) 8, and even insurance (X12N) 10. Today, EDI continues to evolve, integrating with APIs, cloud platforms, and advanced analytics, an evolution that reflects its transition from a hidden black box, back-office process into a visible driver of competitive business practices.
What are the Core Components and Architecture of EDI?
Understanding EDI requires some knowledge of its essential components beginning with foundational standards such as ANSI X12 and EDIFACT, which define transaction sets like the purchase order (850/ORDERS), invoice (810/INVOIC), acknowledgements (997/CONTRL) and Application Advice (824/APERAK). Translation engines through a process known as transformation, convert ERP or business system data into standardized messages while secure communication protocols such as AS2, SFTP, or today’s more modern APIs move these documents between and among trading partner relationships, relationships once guided ONLY through the use of VANS (Value Added Networks). Mappings ensure that each partner’s data aligns correctly with governance guided by partner agreements and real time monitoring through message deliver notifications (MDNs) and functional acknowledgments provide assurance that documents arrive when and as intended.
EDI requires some knowledge of its essential components beginning with foundational standards such as ANSI X12 and EDIFACT, which define transaction sets like the purchase order (850/ORDERS), invoice (810/INVOIC), acknowledgements (997/CONTRL) and Application Advice (824/APERAK). Translation engines through a process known as transformation, convert ERP or business system data into standardized messages while secure communication protocols such as AS2, SFTP, or today’s more modern APIs move these documents between and among trading partner relationships, relationships once guided ONLY through the use of VANS (Value Added Networks). Mappings ensure that each partner’s data aligns correctly with governance guided by partner agreements and real time monitoring through message deliver notifications (MDNs) and functional acknowledgments provide assurance that documents arrive when and as intended.
What are Message Delivery Notifications (MDNs)
When used Message Delivery Notifications (MDNs) indicates that a payload (message) has been received. MDNs are automatically generated by AS2 solutions for transmission back to the sending party. They confirm the delivery , they do not document any formatting errors or loss of data not do they confirm that the receiver’s application system was able to process the message received.
What are Functional Acknowledgments (997s)?
Functional Acknowledgment (997) are industry best practice and are automatically generated by EDI platform solutions for transmission back to the sending party. They confirm the delivery of information and document any formatting errors or loss of data. The Functional Acknowledgment (997) does not confirm that the receiver’s application system was able to process the message received
• Business messages with errors may be accepted or rejected.
• Rejected messages must be corrected and re-transmitted by the sending party.
Should the sending party not receive a 997 it is incumbent on the sending party to find out what happened to the message that was sent and as such should contact their technical support team and the receiving party immediately whenever a 997 is missing.
What is the difference between Message Delivery Notifications (MDNs) and Functional Acknowledgement (997s)?
One of the stated benefits for using AS2 is the message delivery notification (MDN), although some may argue the MDN replaces the Functional Acknowledgement (997), the message delivery notification (MDN) used in AS2 only indicates the message has been received whereas the Functional Acknowledgement (997) the message has been received and confirms the delivery of information and documents any formatting errors or loss of data.
What is the difference between Integrated and Stand-Alone EDI Solutions?
One  of the most important considerations for EDI is deciding whether to adopt an integrated solution or a stand-alone platforms. Integrated solutions can be local or cloud based, can be connected directly into ERP or TMS systems. They simplify workflows and offer automation, automation that may limit flexibility, for example, order can be automated to the point that they can be approved automatically without any human intervention. Stand-alone platforms, by contrast, offer adaptability through frequent human intervention and independence by limiting automation, though they may introduce additional steps or complexity. Modern providers such as PartnerLinQ increasingly offer holistic hybrid approaches which combine the strengths of both models to deliver integration and automation along with visibility, utility, scalability and modularity.
of the most important considerations for EDI is deciding whether to adopt an integrated solution or a stand-alone platforms. Integrated solutions can be local or cloud based, can be connected directly into ERP or TMS systems. They simplify workflows and offer automation, automation that may limit flexibility, for example, order can be automated to the point that they can be approved automatically without any human intervention. Stand-alone platforms, by contrast, offer adaptability through frequent human intervention and independence by limiting automation, though they may introduce additional steps or complexity. Modern providers such as PartnerLinQ increasingly offer holistic hybrid approaches which combine the strengths of both models to deliver integration and automation along with visibility, utility, scalability and modularity.
Why do many EDI programs struggle to get off the ground?
Despite EDI’s clear benefits, many programs struggle to deliver results. common pitfalls such as underestimating the complexity of onboarding new trading partners, relying on rigid or outdated technology, and failing to establish proper governance still occur even within the most experienced organization. Treated as a 'black box' EDI can run unattended which inevitably leads to poor visibility and delayed resolution of issues. While business rules and alerting does resolve many issues, inadequate testing or the absence of a test or DEV environment can exacerbate challenges, turning a strategic advantage into a technical and business burden.
How do I select the Right EDI Solution Provider?
Selecting ![]() the right EDI solution provider is critical for long-term success, organizations should look for providers who can scale with the business and have plans for growth, support rapid onboarding of new trading partners, and integrate seamlessly with ERP and TMS systems. Providers should also offer robust monitoring, real-time alerts, and strong security measures to ensure compliance. Transparency in pricing, reliable support backed by Service-Level Agreements (SLAs) along with a clear innovation roadmap are further indicators of a truly capable, forward thinking partner. Choosing such a provider ensures that EDI will not remain a hidden back-office system within the organization but a visible and strategic enabler of efficiency.
the right EDI solution provider is critical for long-term success, organizations should look for providers who can scale with the business and have plans for growth, support rapid onboarding of new trading partners, and integrate seamlessly with ERP and TMS systems. Providers should also offer robust monitoring, real-time alerts, and strong security measures to ensure compliance. Transparency in pricing, reliable support backed by Service-Level Agreements (SLAs) along with a clear innovation roadmap are further indicators of a truly capable, forward thinking partner. Choosing such a provider ensures that EDI will not remain a hidden back-office system within the organization but a visible and strategic enabler of efficiency.
Are Guidelines & Sample Files for EDI documents available?
Yes. PartnerLinQ provides sample EDI message transaction and implementation guides through its Support and Guideline Management Team.
Sample implementation guides illustrate both inbound and outbound flows, segment layouts, and valid data examples and support testing and partner onboarding. Customized specification documents for use in on boarding and technical development are available upon request.
PartnerLinQ provides:
- Transaction implementation guides
- Sample payloads
- Qualification and testing maps
- Error handling and best-practice notes
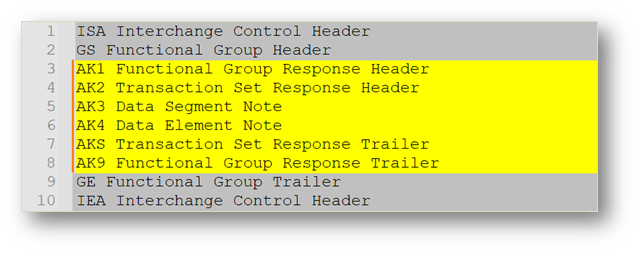
Are EDI Best Practices and Fundamentals available?
Success with EDI depends to proven practices. Establishing and adhering to governance ensures oversight and accountability. Beginning with a pilot and a small set of partners provides a controlled environment to validate mappings and processes before scaling larger transitions. Maintaining a sandbox (DEV or TEST) environment allows safe testing of new changes without affecting production flows. Automated dashboards and alerts prevent issues from disappearing into black-box systems, while tracking key metrics such as onboarding time and error rates support continuous improvement. Documented mappings, automated change and version control further reduces risk and ensures consistency.
Conclusion
EDI basics and fundamentals highlight EDI’s role as both a technological standard and a strategic business tool. Removing black-box inefficiencies and transforming back-office processes into transparent, data-driven operations, EDI empowers businesses to compete more effectively. Modern providers such as PartnerLinQ, can move organizations beyond the basics of EDI into achieving scalability, visibility, and resilience in a very shirt time. Lastly, in today’s digital economy, EDI is no longer just a hidden necessity—it is a visible driver of growth and innovation.
Footnotes:
- What is Electronic Data Interchange (EDI)?
- How Supply Chain EDI Improves Efficiency and Reduces Costs
- Integrated vs Stand-Alone EDI Solution
- Why Do Most EDI Practices Struggle to Onboard New Trading Partners
- A Quick Guide to Selecting the Right EDI Solution Provider
- X12C – Communications and Controls
- X12I – Transportation
- X12M – Supply Chain
- X12N – Insurance
Related Resources

Wayfair transitioned to PartnerLinQ's modern cloud-based EDI platform
<p>
<a href="/case-study/wayfair-transitioned-to-partnerlinqs-modern-cloud-based-edi-platform">PartnerLinQ stands out as the premier supply chain Platform that redefines digital connectivity, end- to-end visibility, and decision intelligence. Built on a resilient technology infrastructure, PartnerLinQ delivers a composable platform that elevates business partner collaboration through accelerated onboarding and orchestrated processes while providing intelligent insights across your entire supply chain ecosystem. With our cutting-edge technology, PartnerlinQ empowers supply chains to seamlessly adapt to dynamic demands at the speed of business.</a>
</p>

Explore Our Integration Solutions
PartnerLinQ Integration Solutions
Connect Everything. Integrate Intelligently.
Future-Proof Your Business with Composable, AI Powered Connectivity.

