You are probably familiar with this ‘BIG VAN’ claim repeated early and often by the champions of value-added networks (VANs):
‘The advantage of the network is the network itself.’
The claim, like all wide-ranging quotes, is to some extent only relatively true. Its validity depends upon who you are connecting with and how actively you link up with your trading partners. A closer look at the flow of goods and information within your business network will possibly reveal that no single network or VAN can address all your B2B/B2C communication needs.
While EDI and, in some instances, the VAN does help you connect, connecting with all your trading partners translates into a significantly higher ROI. EDI today means more than simply X12; it means supporting multiple standards, formats, and transactions from X12, UN/EDIFACT, and GS1 XML trade messages to a number of non-EDI formats like JSON, flat files, text files, and proprietary XML message formats.
Read more: The truth behind the “competitive advantage” of value-added networks
EDI also means accessing a diverse set of communication methodologies – like AS2, MFTP, FTP, SFTP, and APIs – each with their own set of variables. While transaction formats and transportation methodologies make EDI more versatile, the complexity of handling such varied data formats and communication methodologies creates its own set of challenges, particularly when you consider the ‘BIG VAN’ value proposition.
The ‘BIG VAN’ value prop proudly claims that all members in your value chain are available on the same network or VAN as yours; while true to some extent, this is not an entirely accurate assessment. A VAN connection is by all accounts handy and, in some cases, necessary to interact with some trading partners. But it certainly is not everything.
The right tool with the right EDI transportation methods delivers far more effectively than ‘BIG VAN’ and at a lesser cost.
The Significance of the EDI VAN Interconnect
The ‘BIG VAN’ claim is largely backed by the EDI VAN interconnect. The interconnect is a tool that helps your value added network communicate with other value added networks and facilitates exchange of EDI transaction documents between connected pairs of trade partners. The more partners you connect with, the bigger the benefit derived from your communication network.
VAN interconnects effectively reduce friction between and among VANs, while also reducing the need for new VANs. The largest of the VANs reduce VAN-related confusion within partner networks by making claims to connect to thousands of trading partners; in effect though, ‘BIG VAN’ highlights the characteristics of EDI under which all EDI solutions and VAN partners operate.
But what about transactions beyond X12 EDI?
‘BIG VAN’ and the interconnect rely on a steady stream of ISA and GS identifiers within X12 transactions to move data, without which the ‘BIG VAN’ is about as useful as a cell phone without buttons. While the VAN connection does handle X12, what about images, APIs, or XML files? These are typically not included in ‘BIG VAN’ offerings and, in most cases, require a different product altogether, adding to your overall cost.
A closer look at the VAN interconnect reveals that the reality of ‘BIG VAN’ is very different from the claim; if the interconnect connects ALL VANs then ALL VANs have the same access to trading partners, which means that ‘BIG VAN’ has a very different concern. ‘BIG VAN’ is concerned that it will inevitably be relegated to the stature of an ‘Ordinary VAN’ and without reservation.
‘BIG VAN’ makes a big claim and living up to that claim is becoming nearly impossible. This makes all ‘small VAN’ operators a competitive threat – why else would ‘BIG VAN’ make such claims if not to control and confuse the market? The VAN interconnect and image files remove the confusion from the claim ‘the advantage of the network is the network itself’; what else is there to the reality of ‘BIG VAN’?
The Synergy
Architecturally speaking, an EDI solution is actually made up of three components (or solution layers, if you’ll pardon the expression) – the transportation, transformation, and integration layers. While EDI is very effective when it leverages a ‘VAN’ connection, the VAN component is only a fraction of EDI, less than 30%.
Think about your VAN connection in the same way you think about how your mobile phone functions. Your mobile phone functions by combining the services provided by the phone manufacturer, an infrastructure provider, and a telecom company; similarly, EDI functions by leveraging the synergy of these component layers to work as a synchronous whole.
Components of the ‘VAN Solution’
- Transportation. Along with VANs, this layer works using many other methodologies such as AS2, MFTP, FTP, SFTP, and APIs. Most of these methodologies have been around for a couple of decades now. Your VAN, in fact, may still be using FTP to connect you with your VAN mailbox; if it is not leveraging FTP, it is likely using AS2. Get in touch with your EDI team representative and ask, they should be able to tell you.
- Transformation. The transformation layer facilitates translation between different (EDI) formats. Formats like X12, UN/EDIFACT, GS1 XML trade messages, JSON, flat files, text files, or proprietary XML messages are transformed into formats that your ERP systems can easily understand and use.
- Integration. In the final layer, the transformed message is available to be consumed by the ERP. API connectors have been introduced in recent years to connect you with your ERP in a normalized way, much like the ODBC connector you may have used in the past. The integration layer can be an API or a connector like ODBC or ODATA – the main emphasis here lies in providing (a) the route for landing the messages and (b) feedback that lets you know whether the order was rejected or accepted. The latter is the target, which requires the least manual input.
Do More Connections Provide More Benefits?
The key word is ‘choice’. If one network has the potential to provide a competitive advantage, do multiple networks offer even greater benefit?
The quantity of available networks is only one criteria that determines how effective your network is. Connecting to multiple VANs is, frankly, a drain on resources, particularly when all VANs make use of the same VAN interconnect.
While there is a need to be mindful of the connections available to your trading partners, using multiple VAN connections to stay in touch makes no sense at all. It is like having two or more cell phones or cable TV subscriptions, particularly when methodologies like AS2, MFTP, FTP, SFTP, and APIs are available. Many of these options have low or no cost associated with them while VAN costs are subscription based and incur transaction fees that need to be paid monthly, much like that second cell phone that we referenced earlier.
The AS2 Effect
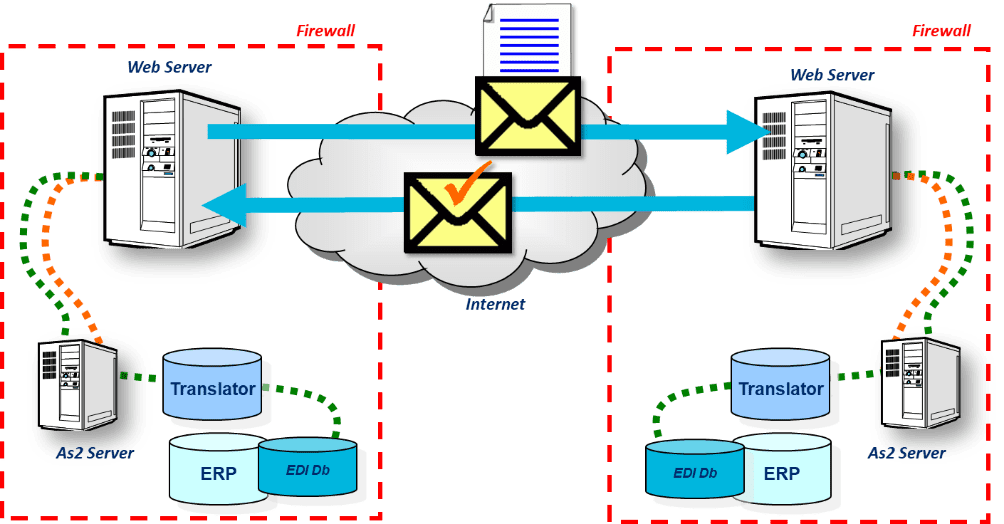
Application Statement 2 (AS2) is used for a reliable and secure transfer of data over the Internet. It provides a direct, unhindered connection with a trading partner and delivers document receipts and real-time tracking without requiring a VAN or a VAN interconnect. Your standard internet connection serves as the transportation layer; it is payload-agnostic, which means you can use the same tool to transmit images and every business has internet connectivity today.
Unlike a VAN, AS2 does not typically have monthly charges or transaction fees. It reduces the chances of transaction failure by establishing a one-to-one transmission channel, without the need for a middle man, a VAN interconnect, or a ubiquitous VAN. Also, there is a Message Delivery Notification, but more on the MDN at a later time.
Putting It All Together
Now that we have unpacked the ‘BIG VAN’ claim, we can conclude that your EDI solution should provide more than one communication channel, has to be capable of handling a wide range of EDI formats, and MUST integrate smoothly and automatically with your enterprise systems.
We’ve also come to the conclusion that ‘BIG VAN’ cannot support the features that you need without complicating matters with additional software and subscriptions.
That’s why PartnerLinQ is different. PartnerLinQ is not a VAN; rather, it is a highly scalable, dependable, and configurable EDI and B2B communication solution. PartnerLinQ is ‘integration without complication’ that supports integration with Microsoft Dynamics 365 and other ERP systems. It includes an AS2 solution, FTP, MFT, and SFTP and can connect with any VAN, making it the perfect tool for B2B/B2C communication for your EDI and non-EDI partners.
PartnerLinQ also supports API-based ecommerce platforms like Shopify and Magento out of the box, providing your organization a seamless shift between EDI and API integrations; there’s nothing to add and nothing to buy, it’s all in there.
The solution also operates seamlessly between EDI and non-EDI formats – from X12, UN/EDIFACT, and GS1 XML to non-EDI formats like XML and JSON. While there are too many formats to list in a blog, this is a crucial factor that make PartnerLinQ a perfect choice for your EDI, B2B, and API integration and for smooth communication, while decreasing your reliance on ‘BIG VAN.’
 PartnerlinQ
PartnerlinQ