Supply chains are a complex orchestration of people, places, and things. Globalization, pressure from competitors, and increasing customer expectations have all combined to push organizations towards expanded and diverse partner networks, and for Transportation Services and Logistics providers (TSLs), the landscape is even more complex.
Y. Hata & Co., Limited has been an essential part of Hawaii’s economy for more than 108 years. Yoichi Hata and his wife started the company as a “mom-and-pop” operation in 1913, selling products (wholesale) out of a family garage on the Big Island of Hawaii. But the visionary founder soon transformed the modest backyard operation into a prolific statewide network.
The PartnerLinQ Advantage: 5 Key Value Adds for Food and Beverage Supply Chain Optimization
Foodservice on the Rebound?
Consumer interest had increasingly tilted towards experiences like travel, movies, and entertainment over the last decade. So being homebound over a year and a half has naturally created a void in people’s lives, with a craving for activities that create memories and provide entertainment. This was reflected by an immediate increase in restaurant transactions when municipalities tentatively eased restrictions for on-premises dining in 2020. And following a widespread rollout of vaccines in the US, consumers are becoming more confident about eating out. The first signs of a shift in spend pattern are already evident. The US Census Bureau’s Advance Monthly Sales for Food Services1 show a surge in April sales for food services and bars, with dollar sales up 15% from a pre-pandemic 2019 and a whopping 116.8% over last year. As per a NielsenIQ survey2, 62% of Americans miss eating out at restaurants the most and 28% of households are planning more trips to restaurants and bars than they did in 2020.
Reimagining Customer Experiences
Foodservice outlets are also innovating in terms of customer experiences and product offerings as their buyers still prefer contactless, hands-off transactions. Quick-service giants like McDonald’s and Burger King are redesigning premises3 with smaller dining rooms, more pick-up options, and a distancing of store operations from guests. Some like Maggiano’s are presenting a whole line of pre-cooked meals for consumers to take home and eat later. As restaurants desperately try to recapture lost sales, they are boosting up their catalog of digitally-delivered meals to ease household cooking burdens and provide in-home restaurant experiences. New methods of delivery like on-demand food trucks and in-garage grocery delivery services are picking up, while brands like Albertsons, Domino’s, and Kroger are experimenting with sophisticated technological alternatives like robots, drones, and driverless delivery services.
Food and Beverage Supply Chain Optimization: A Continuous Process
But the F&B industry also needs to continue looking for ways that optimize supply chain and partner networks in order to meet quickly evolving market demands. Many food makers and distributors are facing impediments like labor shortages, supply constraints, and high freight costs, which make it difficult to deliver all their products on time. Retailers had overlooked such deviations for months during the pandemic. But they are less willing to accommodate now as companies strive to get back to business-as-usual amid a reopening economy. Big buyers like Walmart are imposing chargebacks on suppliers for late deliveries or incomplete orders, while Kroger has launched a new ‘supplier discovery program’ to add new, diverse, and more reliable suppliers for farm produce, bakery, meat, seafood, and dairy.
On one hand, friction between food retailers and their suppliers adds costs across the food value chain. On the other, end-consumers are struggling to come to terms with job losses or other financial hardships brought on by the COVID-19 pandemic. Buyers are growing increasingly more price sensitive; IRI data4 indicates that a 10% increase in the price for edible products could reduce sales volume by as much as 17%.
The PartnerLinQ Advantage
To fully utilize a period of increased demand, PartnerLinQ provides food service organizations a number of distinct advantages to extract maximum value out of their supply chains.
Easy Partner Onboarding
F&B companies need to rapidly onboard new sales channels and supplier partners to take advantage of opportunities as and when they emerge. PartnerLinQ supports EDI communication as well as direct B2B transfers to and from non-EDI organizations. It also supports a wide range of common data interchange standards to ensure reliable and secure communication across partner networks. With its EDI-optimized business rule engine and extensive preconfigured business rule library, PartnerLinQ increases the flexibility to connect with partners on their own terms and makes it possible to respond faster to partner-driven changes.
Automated End-to-End Workflows
PartnerLinQ’s infinite job scheduler allows organizations to configure, schedule, and execute multiple transactions simultaneously, including features like a bulk transfer of business-critical data to trading partners without any human intervention and without interfering with other business processes. Removing hands-on processing means that F&B organizations can ensure fewer errors and improved customer relationships, leading to improved delivery of goods and services and reduced customer turnover. A streamlined and automated communication process enhances compliance and helps avoid fines due to SLA breaches, payment delays, and performance gaps. PartnerLinQ’s built in auditing functionality gives F&B organizations the information to combat chargebacks and provide proof of delivery to end customers.
Smarter B2B Integration
PartnerLinQ integrates natively with Microsoft Dynamics 365 and can be integrated with other ERP systems at the same time without the need for additional licensing or subscriptions. It also provides robust support for EDI integration with dozens of ERP systems and ecommerce platforms. This allows foodservice businesses to shift seamlessly between EDI ERP and API-based integrations and with corporate parent companies or wholly owned subsidiaries at the same time, making support and maintenance more efficient, more attractive, and less vulnerable. F&B organizations can enjoy seamless connections with all network partners and a variety of internal systems while deploying multiple supply chain solutions within a single platform.
Hybrid Cloud Architecture
The food supply chain software ensures a simple and robust cloud deployment that minimizes infrastructure costs and enhances analytical reporting powered by Azure’s serverless, scalable, event-processing engine. A hybrid cloud architecture provides the most agile, flexible, and frictionless way to exchange B2B data, enabling further F&B supply chain optimization and empowering foodservice companies to take on the complexities of a multi-enterprise, multi-application integration process. In addition, they can now enjoy real-time visibility to garner insight and control across the entire value chain.
Omnichannel Integration
PartnerLinQ’s multi-channel integration capabilities allow it to combine perfectly with a Headless Commerce architecture, which separates the front- and back-end of an ecommerce solution to enable faster and more flexible customer experiences. It is also aligned with a unique CSP program and a layer of API integrations, delivering tailored experiences unique to customer preferences.
Gearing Up for the Next Normal with PartnerLinQ
In addition to a digitally-empowered F&B supply chain optimization, PartnerLinQ helps foodservice companies increase throughput, establish and enhance supplier relationships, keep track of deliveries and stay on schedule, while reducing chargeback risk and taking on new market opportunities and additional channels in the new normal. PartnerLinQ’s food supply chain solution also helps manufacturers keep traceability in house, remain in line with customer preferences, and increase connectivity across channels – both traditional and e-commerce.

Endnotes:
- https://www.census.gov/retail/marts/www/marts_current.pdf
- https://www.nielsen.com/us/en/insights/article/2020/understanding-consumer-sentiment-can-help-companies-adjust-as-the-u-s-begins-to-re-open/
- https://www.bakingbusiness.com/articles/53819-foodservice-adapts-new-concepts-as-it-recovers
- https://www.iriworldwide.com/en-us/insights/publications/cpg-pricing-promotion-revenue-growth-during-inflation
VAN Independence: How Does a Trading Partner Break from Its VAN?
What’s Your VAN Independence Strategy?
Independence Day is now behind us and summer is nearing its end. The 4th of July holiday encourages reflections, reflections that include independence and country. It also includes independence in financial, personal, and business matters. Returning to work following the mid-summer holiday this year, I began to think about systemic independence – specifically the independence of trading partners who are more willing than ever to declare themselves independent from their VAN.
A value-added network (VAN) is a private network used by a company to facilitate and ensure the exchange of EDI transaction documents with one or more trading partners.
Communication
Traditional EDI includes costs of configuration, transformation, integration, and communication. EDI communication typically includes the use of a VAN. EDI requires a mechanism that allows trading partners to send and receive messages. While there are other methods, the VAN is the most conventional one.
There are many such VANs available, typically through subscriptions. These VANs communicate with members as well as among each other, allowing VAN subscribers to communicate with one another regardless of the community to which they belong.
Foundation
The original VANs were much more than what service-based organizations associated with a transport mechanism. Many began their lives as services associated with “computing time” back when computers were rare and the needs for computing were greater. Companies like IBM set up massive communication channels using the IBM Systems Network Architecture (SNA) to facilitate the use of mainframe computers; such interactions and transaction exchanges were subsequently moved to smaller and smaller machines using File Transfer Protocol (FTP).
Domination
Once in place, VANs began reducing the services they provided. No longer providing computing services, they set their sights on becoming massive communication channels. They set up their own independent communications networks, complete with “mailboxes” and “interconnects”. The mailbox was an address on a VAN used by a trading partner to pick up and drop off transaction documents. On the other hand, the interconnect was a tool used by VANs to communicate with other independent VANs to help delivery and exchange of transaction documents.
Substitution
Once in place, VANs began reducing the services they provided. No longer providing computing services, they set their sights on becoming massive communication channels. They set up their own independent communications networks, complete with “mailboxes” and “interconnects”. The mailbox was an address on a VAN used by a trading partner to pick up and drop off transaction documents. On the other hand, the interconnect was a tool used by VANs to communicate with other independent VANs to help delivery and exchange of transaction documents.
So why aren’t more companies moving to AS2? It may be because no one has explained the benefits in a way that makes a comparison easy.
Explanation
AS2 securely moves more data at a lower cost by relying on Internet access rather than a dedicated network. The VAN’s monthly access fees and kilo-character costs disappear.
AS2 relies on software and the Internet to accomplish the same tasks that were once only found in the domain of VANs.
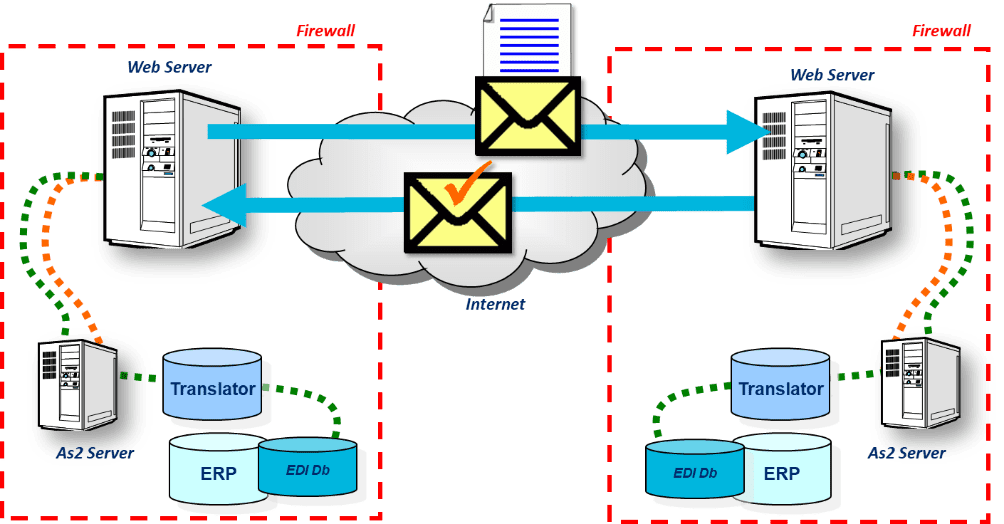
Erosion
Market consolidation of EDI products and services has recently seen a consolidation of VANs, with many of the impacted customers moving toward AS2. Considering the growth rates we saw in the use of “free email” in the browser wars of the 1990s, industry experts agree that AS2 is likely to become more like FTP in its frequency of use.
What’s the Lesson?
EDI buyers will look for an EDI solution that:
- Offers independence from the VAN, can leverage any type or number of independent connections, and is in tune with today’s market
- Has a willingness to go that extra mile for their business
- Provides improved service offerings at a fixed cost and includes everything they need to make it work
- Integrates directly with their ERP, works without manual intervention, and helps them be more efficient.
Questions to Ask Your Client
- Are you happy with your current EDI solution?
- Is your EDI solution integrated or does it require manual intervention like logging into a portal, uploading spreadsheets, or running a batch process to make it work?
- Are you using multiple solutions to communicate with your trading partners?
- How would you like to break from these dependencies?
- Would you be interested in hearing about a frictionless EDI solution?
Pagination
- Previous page
- Page 3
 PartnerlinQ
PartnerlinQ




